Public services
| Name | Description | ELIXIR Node | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Patents
|
Our contribution to innovationUsing The Lens, a patent and scholarly literature search facility, we find that ELIXIR resources are increasingly mentioned by name in patent applications. This is a clear indication of their usefulness to bioinformaticians of all sectors (academic, industry), and across the globe. We will soon expand our search to cover all ELIXIR resources, a number of which existed before ELIXIR became operational as a distributed research infrastructure. Our approach is loosely inspired from earlier ELIXIR work (Bousfield et al. 2016), but less computationally intensive, yet lightweight and repeatable so as to operationalise it as an indicator. This is considered to be a qualitative exercise as identical patent applications are known to be submitted in various jurisdictions by their authors. EP: European Patent Office. Access the full visualisations in tableau. Support from the EU-funded PathOS project. Impact areas to which we contributeUsing a simplified interpretation of the International Patent Classification (IPCR), patent applications mentioning ELIXIR resource names can be visualised by main fields of use. The qualitative and high-level visualisation below summarises the main impact areas to which ELIXIR resources contribute. Note that many patent applications list several IPCR classes, and that tile size is only loosely related to the number of mentions. Access the full visualisations in tableau. Support from the EU-funded PathOS project. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Pathogen Data Focus Group
|
IntroductionThe Pathogen Data Focus group aims to establish the basis for a distributed and interoperable network of regional and national pathogen data hubs. GoalsThrough a joint effort, the Focus group will work towards:
The Focus group will invite experts and stakeholders to join in this concerted, expert-driven effort towards sustaining and ensuring high-quality data for global surveillance and research. Mailing listpathogen-data@elixir-europe.org Leadership
(ELIXIR Switzerland) 
(ELIXIR Spain) 
(ELIXIR Norway) 
ELIXIR Hub Liaison |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PDF test
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Professionalising Careers in Research Infrastructures
|
As a research infrastructure (RI), ELIXIR relies upon a diverse range of roles, such as trainers, data stewards, project managers, software engineers, developers, community managers. By highlighting the career options within a research infrastructure, we aim to promote interest in these roles to support the career development of researchers beyond the traditional academic paths of, for example, Principal Investigators. As well as supporting the research community by recognising infrastructure career paths, this Focus Group will actively contribute to ELIXIR's commitment to diversity and inclusion within the research ecosystem. Goals of the groupInitially, the Focus Group will conduct a comprehensive survey of existing job advertisements channels (including the past activity) within ELIXIR in order to classify roles (assessing function, hierarchical position, required skills, etc). The planned outcome of this mapping exercise will enhance the compatibility of job titles and clarify the relationships among different roles within ELIXIR. The Focus Group will also collaborate with external projects with a related aim, such as ARISE, Technician Commitment, BioNT, CTLS, SciLifeLab Training or EOSC projects as well as internal ELIXIR projects and entities like ELEAD, ELITMa, RItrain(Plus), the RDM Community and RDA Focus Group , eRImote, the Impact Focus Group and the Training Platform. Mailing listri-career-paths@elixir-europe.org Group chairs
(ELIXIR Germany)  (ELIXIR UK)  (ELIXIR Sweden)  (ELIXIR Hub Liaison) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RDM Trainer Network
|
The ELIXIR RDM Trainer Network brings together life sciences professionals working in upskilling, training or educational activities around RDM and Data Stewardship. We aim to be the enablers of knowledge exchange, a hub for sharing relevant training materials and discussing common challenges across the life sciences in RDM training. Ways to gets involved
Who the Network is forRoles working with Life Science data, irrespective of career stage, such as:
The Network is open to anyone interested in life science data management training, even outside ELIXIR. Leadership
(ELIXIR Germany) 
(ELIXIR Germany) 
(ELIXIR UK) BackgroundThe RDM Trainer Network, part of the RDM Community was conceived by the ELIXIR Training Platform during the ELIXIR-CONVERGE project (WP2). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Research Data Management Community
|
Research Data Management (RDM) is central to the implementation of the FAIR (Findable Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) and Open Science principles. Recognising the importance of RDM, ELIXIR Platforms and Nodes have invested in RDM and launched various projects and initiatives to ensure good data management practices for scientific excellence. These projects have resulted in a rich set of tools and resources for FAIR data management. However, these resources remain scattered across projects and ELIXIR structures, making their dissemination and application challenging. Therefore, it is important to coordinate these efforts for sustainable and harmonised RDM practices, with dedicated forums for RDM professionals to exchange knowledge and share resources. Goals of the CommunityThe ELIXIR RDM Community will bring together RDM experts to develop ELIXIR’s vision and coordinate its activities in order to take advantage of the available RDM assets. It aims to coordinate RDM best practices and provide an overview of how to use the existing ELIXIR RDM services, in close collaboration with ELIXIR Platforms, Communities and Focus Groups. The expected members of the Community are life science RDM professionals in academia and industry in ELIXIR and beyond. The scope of the Community is:
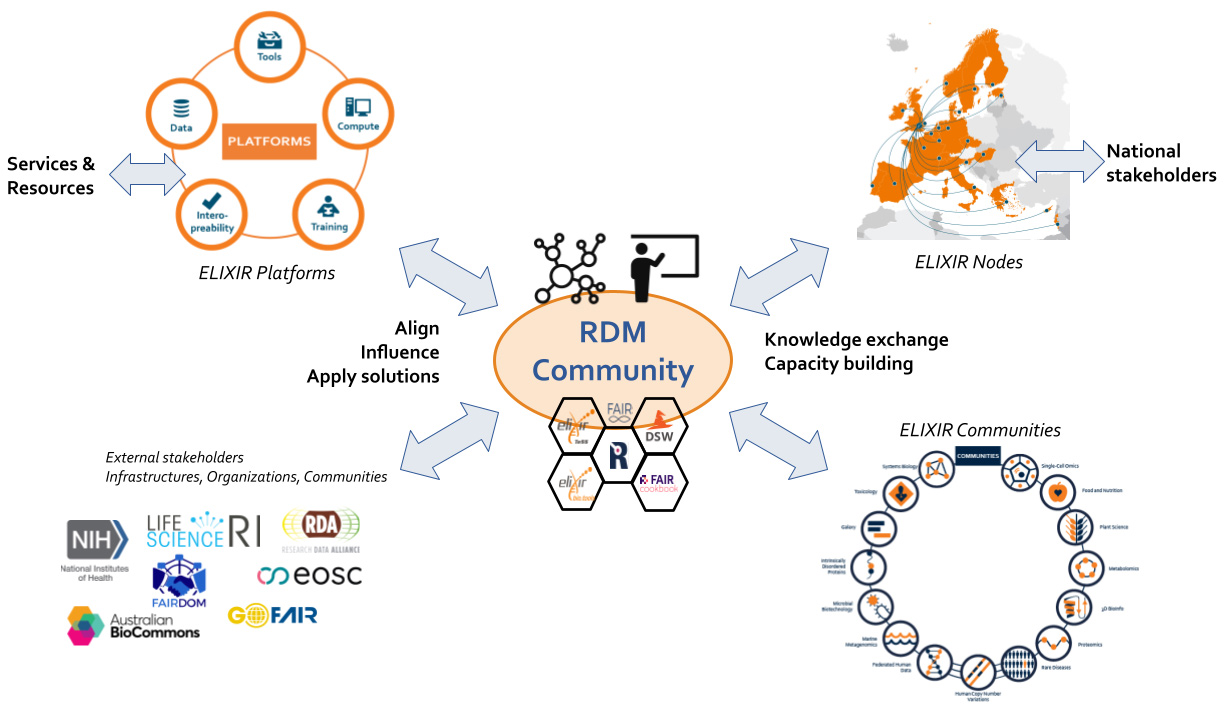 The initial objectives of the RDM Community focus on sustaining and consolidating the outputs of previous initiatives and projects into a unified structure. This falls into four main areas: People network
RDM knowledge
RDM training
External stakeholders
Leadership
(ELIXIR UK) 
(ELIXIR Belgium) 
(ELIXIR Sweden) 
(ELIXIR Netherlands) 
katharina.heil@elixir-europe.org (Communities Liaison, ELIXIR Hub) Find out more
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Review general Recommendations from Galaxy Working Group
|
The Galaxy Working Group has compiled a set of potential recommendations to send the Heads of Nodes (HoNs). This is a short 2 page document includes a simple table where we classify each recommendation we have collected from different sources. These sources include a) the ELIXIR-Galaxy BoF in July 2015, b) a survey distributed throughout the ELIXIR constituency and the Galaxy Community Conference 2015 and c) the ELIXIR All Hands Breakout on Galaxy (March 2015) and follow up discussions by the TeCG. This set of recommendations will be the basis for the final document to be submitted to HoNs (which we will share for feedback next week). To minimise bias and maximise inclusivity we would now like to request feedback from as many of you as possible. We will have this recommendations table open for discussion until Friday 25th of September.
This is the document link: Many thanks in advance and best regards, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Scientific Advisory Board (SAB)
|
The Scientific Advisory Board plays a major role in the process for reviewing and selecting ELIXIR Nodes and provides strategic scientific advice to the ELIXIR Board. The SAB is an independent body, made up of leading experts from around the world. The committee also includes two independent ethics advisors to advise on ethical, legal and social issues related to ELIXIR. The ELIXIR SAB meets twice a year. What the SAB does
SAB members
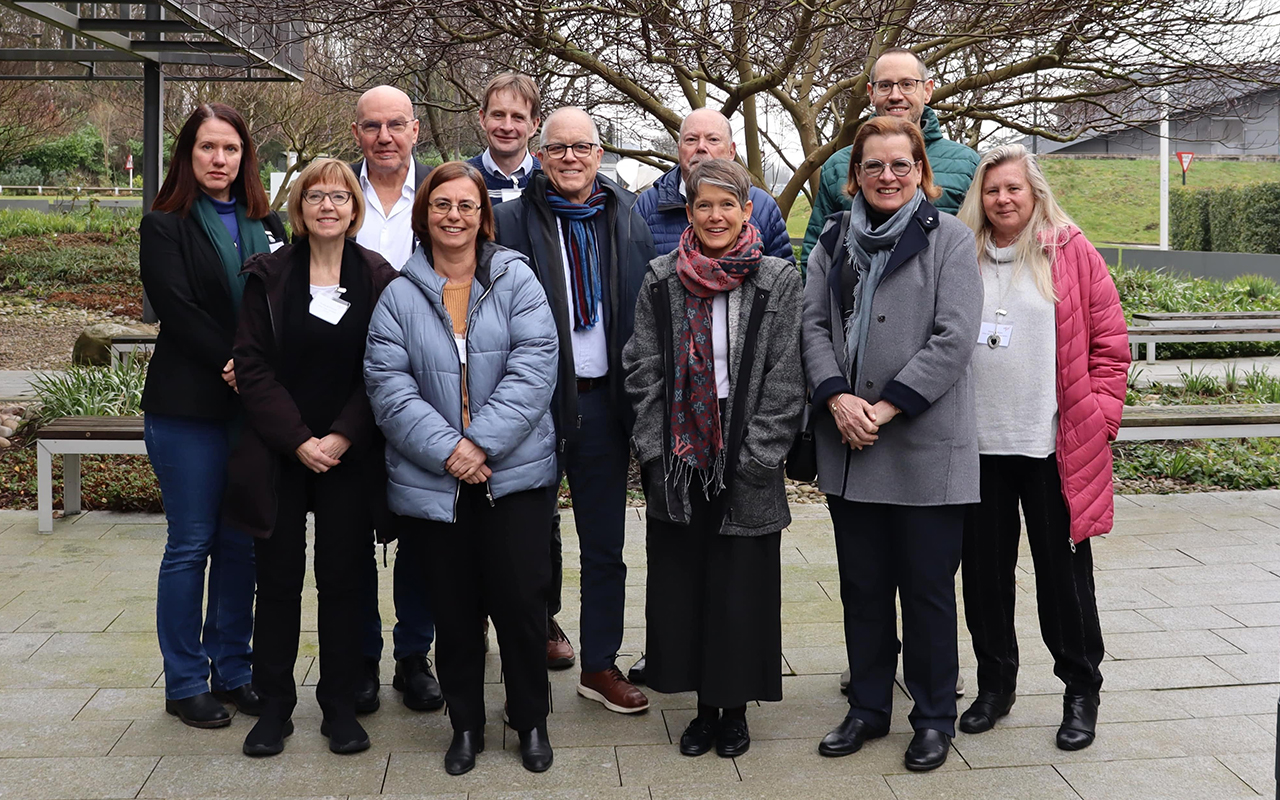
Members of the SAB at the February 2025 meeting (from left to right): Janet Kelso, Fiona Brinkman, BF Francis Ouellette, Luisa Pereira, Paul Kersey, Eric Meslin, Philip Bourne, Danielle Kemmer, Bartha Knoppers, Augusto Rendon, Doreen Ware |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service Collections Framework
|
 The SCF is a guide to help ELIXIR Communities, Focus Groups, Platforms and Nodes to develop ELIXIR Service Collections, showcasing ELIXIR Service use in thematic areas.
Log in to view the full description of the framework, with a more detailed diagram FAQsWhat is the SCF?SCF stands for Service Collections Framework. It is an impact-informed guide that helps ELIXIR’s Service portfolio to be showcased in a manner that highlights service utility reflecting scientific use cases. Why is the SCF needed?To identify avenues for showcasing ELIXIR Service uses through Thematic Service Collections, with an emphasis on wider engagement of the global life sciences community - a key to sustainability. What are Thematic Service Collections, and how are they different from the SCF?Thematic Service Collections are produced by the SCF, and help to contextualise and highlight ELIXIR Services for scientific use cases. These are intended for the benefit of the wider life sciences community, and help life scientists to find and access requisite bioinformatic resources, as well as gain skills and adopt good practices and standards to meet their scientific and professional needs. Who are the users of the SCF and the Thematic Service Collections?The SCF is targeted at users across the ELIXIR structures (Communities, Focus Groups, Platforms, Nodes). ELIXIR’s Platforms enable continued Service provision, and are used when developing Thematic Service Collections. Why does the SCF emphasise outreach and community engagement?To showcase and disseminate ELIXIR Services in life sciences research. How does the SCF help with sustainability?The SCF is designed with emphasis on ‘outcome and impact’ for service provision and their use cases. It explicitly encourages a staged development of Thematic Service Collections to aid visibility, outreach and community engagement for sustainability of ELIXIR Services its Research Infrastructure role in facilitating life sciences research How does the SCF help funders and stakeholders?By providing evidence of ELIXIR Service utility in various thematic areas, scientific discoveries and output. For more information on ELIXIR Impact areas, see Figure 1, Martin et al. (2021). Can non-ELIXIR services be included in the Thematic Service Collections?Yes, subject to review where no existing ELIXIR Service covers the identified need for a specific collection. By principle, ELIXIR aims to reduce effort duplication, hence it will encourage the inclusion of existing and FAIR services that fill gaps in its Service portfolio. What if I cannot fit my service use into any of the SCF categories?The SCF is designed with due consideration to ELIXIR’s internal workings. It comprises 6 categories: ‘Computational tools, data and infrastructure’, ‘Scientific workflows’, ‘Data management’, ‘Industry engagement’, ‘Anticipatory & Responsive deployment,’ and ‘Outreach & community engagement’. If you are unsure about any aspect of the SCF and its use, please reach out for further information and advice. Can external parties use the SCF and generate Thematic Service Collections?Yes. In alignment with open science principles, anyone is free to use the SCF to develop collections that meet their use case. However there is limited support for non-ELIXIR members to generate Thematic Service Collections. How do the Key Service Collections relate to the Thematic Service Collections?The Key Service Collections (e.g. Core Data Resources, ELIXIR Deposition Databases, Recommended Interoperability Resources) can be included as part of any Thematic Service Collections. The Key Service Collections are developed through a formal selection process led by ELIXIR. How does the SCF and Thematic Service Collections support open science?The Service Collections help make services more discoverable by users, hence relate to the F (findable) in FAIR. Using the SCF to develop Thematic Service Collections helps the life sciences community in their work, as well as motivates service improvements. If you use ELIXIR Services or help inform ELIXIR’s Service portfolio, then you are already supporting open science. The ELIXIR Service label is a mark of reliability, quality, open community contribution, and sustainability for life sciences and bioinformatics resources. The more these Services are used, the more useful they become.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Set up the Owl and other microphones
|
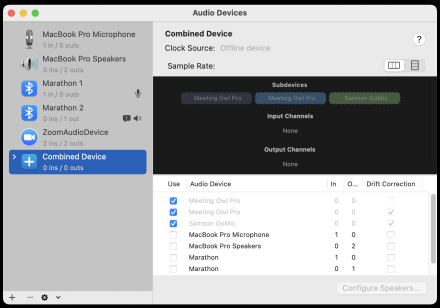
Meeting Owl ProThis device contains multiple cameras, microphones and speakers in a single unit. The cameras that will cover a whole room (380 degrees) and can detect and focus on up to three individual speakers simultaneously. The microphones will cover a room with up to 12 people (more than this and the voices are a bit quiet). The speaker is loud enough for a considerably larger group. The Owl is controlled by an app (search "Owl Labs") which also makes it is possible to connect two together. If you are using a Mac, it can also link up with other microphones enabling a much wider coverage (see below). To set it up
Samson Go MicThe Hub has four small microphones available as part of a kit, including extension cables, 4:1 hub etc. One microphone will cover up to 10-12 people in a meeting, using more will ensure everyone is picked up clearly.  For a single microphone, simply plug the cable in and select the device from the Zoom pop-up menu. Settings button (side)
Alternatively, connect multiple devices as shown in the diagram above and follow these instructions: Combine devicesMacs have a tool to merge multiple microphones into one, making them visible to Zoom etc.
Complete the set up
Notes
Software Updates
Any questions or if these details need updating please contact david.lloyd@elixir-europe.org. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Single-Cell Omics Community
|
Single-cell and spatial omics (SCO) has revolutionised the way and the level of resolution by which life science research is conducted. It has not only impacted our understanding of fundamental cell biology, but has also provided novel solutions in cutting-edge medical research. The rapid development of single-cell and spatial technologies has been accompanied by the active development of data analysis methods, resulting in a plethora of new analysis tools and strategies every year. Such a rapid development of SCO methods and tools poses several challenges in standardisation, benchmarking, computational resources and training. These challenges are in line with the activities of ELIXIR. The ELIXIR Single-Cell Omics Community aims to identify the main challenges in single-cell and spatial omics research and coordinate an international effort to best serve the needs of researchers. The Community will build on top of national experiences, and pave the way towards integrated long-term solutions for SCO research. 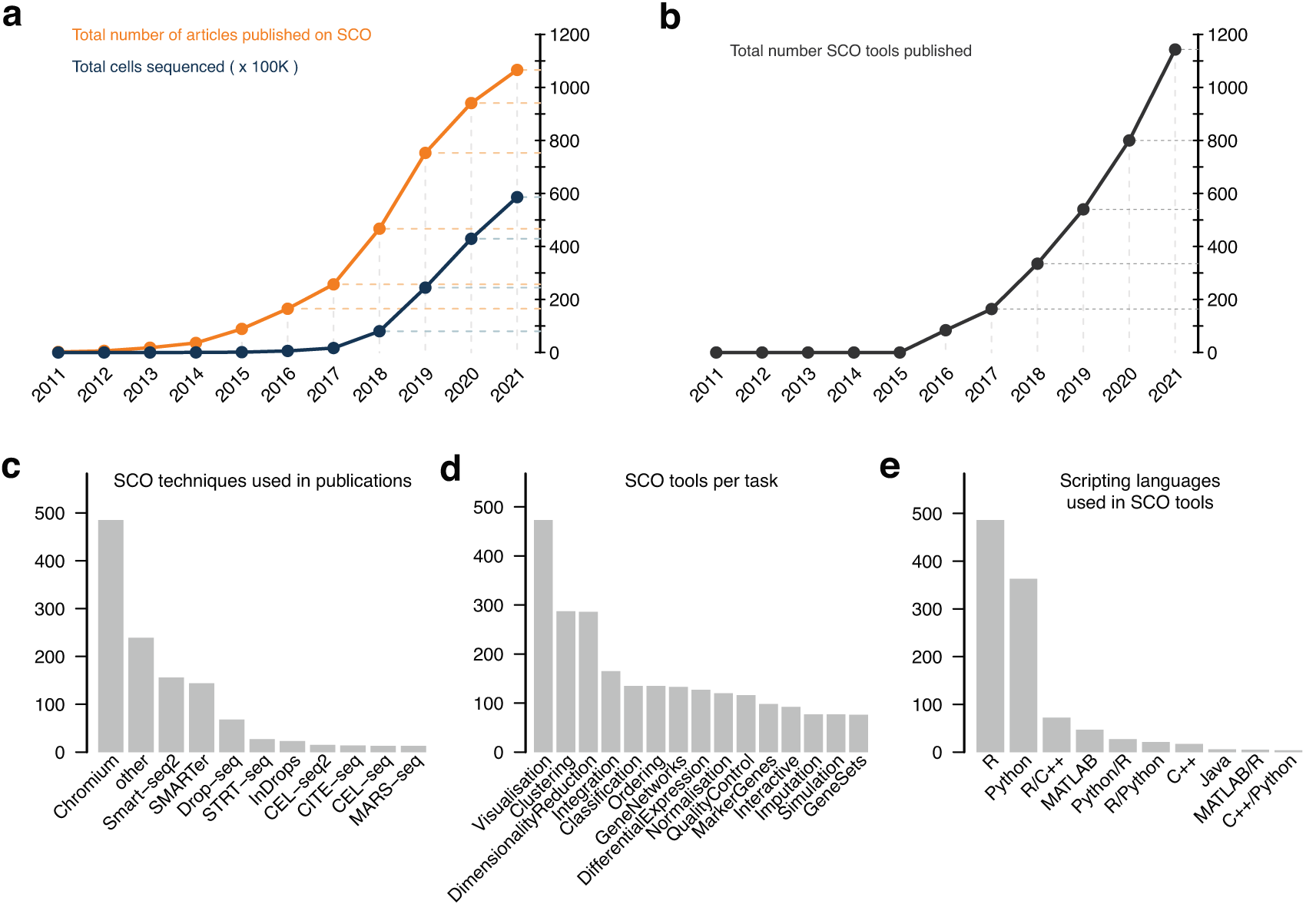 Goals of the CommunityThe SCO Community has outlined key focus areas in their whitepaper on F1000Research. In the initial phase the Community aims to address issues in: TrainingThis is the core goal of the Community. Please see the training section of our website for more info.
Standardisation and interoperabilitySeveral standards exist in the field of Single-Cell Omics (e.g. FASTQ, FAST5, BAM, CRAM), while a few processed data formats are starting to converge (e.g. tab-separated files, AnnData, HDF5, loom, SingleCellExperiment, Seurat, scverse). However, many of these have had to change in order to adapt to new technological advances that rendered previous formats inadequate.
Identifying the most appropriate and performant analysis toolsA plethora of SCO tools exist, and yet standards on how to benchmark or evaluate the accuracy of each tool are lacking. Furthermore, most benchmark efforts are focused on certain cell types or tissues. Please see the benchmarking section of our website for more info.
Leadership
(ELIXIR Italy) 
(ELIXIR Germany) 
(ELIXIR Finland) 
katharina.heil@elixir-europe.org (Communities Liaison, ELIXIR Hub) Find out more
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ELIXIR AAI for home organisations
|
The ELIXIR AAI was migrated to Life Science Login in April 2022. The Life Science Login, a common user authentication and authorisation service for the Life Science (LS) research infrastructures (including ELIXIR) was launched on 11 April 2022, and the ELIXIR AAI was migrated to it. Home organizations now integrate with the Life Science Login. See the LS Login page for Home Organizations for detailed information. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ELIXIR AAI for service providers
|
If you are a service provider, you can integrate with the AAI using standard protocols like SAML 2.0 or OpenID Connect. When a user wants to log in to your service, you redirect them to the AAI for authentication. Once they are authenticated, you will receive information about the user (attributes), such as their name, identifier, affiliation, group memberships, and authorisations. The ELIXIR AAI was migrated to Life Science AAI in April 2022. However, some of the ELIXIR AAI's features are not yet available in LS AAI. To rely on those features, you need to integrate to the Legacy ELIXIR AAI, instead. Before registering your service, please check first if your service needs any of the features in this list.
Useful links
Training
Instructions for services to be connected to the Legacy ELIXIR AAINote: for services to be connected directly to LS AAI, please refer to the LS AAI instructions. How to integrate your service with the Legacy ELIXIR AAI
Complete instructions
You can find a complete list of online training and webinars in TESS (ELIXIR's training portal). Instructions for Services connected to Legacy ELIXIR AAINote: the ELIXIR AAI team will contact the services separately on migration to LS AAI. See the ELIXIR migration news for more information. How to manage your service registrationYou can manage your service registration via the ELIXIR SPReg application. How to ask Legacy ELIXIR AAI to manage access to your servicesIn general, you can configure the Legacy ELIXIR AAI to manage access to your services by creating user groups in the Life Science AAI, adding users to those groups, and then assigning different groups to different services. The setting "Restrict access to the service based on membership in groups" in SPReg enables this functionality. When access control functionality is enabled for the service, a user accessing the service needs to have:
Based on the further configuration of the service, if the user does not meet the criteria above, they can be redirected to an unauthorized page, a specific page of your choice, or offered to register into the configured groups. See the managing access to services document for more information on the functionality. How to set up a separate Acceptable Usage Policy in the Legacy ELIXIR AAIAn Acceptable Usage Policy can be set up by the management and service administration in your organisation. See the detailed instructions or check the slides. Enforcing authentication via a particular Identity ProviderYou can force the users to authenticate with a particular Identity Provider, and bypass the "Choose how to log in" page. See Hinting the IdP to be used in the authentication process. How to implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)The ELIXIR Legacy AAI supports so-called "step-up" authentication. You can ask the user to perform MFA, so that the user performs MFA with their home organization (if supported), or they make use of the ELIXIR's own MFA service. ELIXIR MFA is currently supporting several MFA methods. Users can use their smartphone application to generate a unique six digit code, use a WebAuthn capable token (i.e. FaceID device, YuiKey), or get a uniquely generated code for recovery purposes. Register the MFA capability as a user. You will be asked to enroll a TOTP token. After that, you can enroll more TOTP tokens, WebAuthn tokens, and generate the recovery codes. What GA4GH passports and visas are, and how to implement themThe ELIXIR AAI implements the Passport specification of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH), describing the syntax and semantics for expressing a user’s access rights to registered and controlled access data. See GA4GH passport support in the Legacy ELIXIR AAI. Demos: Demo on transferring data access permissions from REMS to EGA |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Towards Data Stewardship in ELIXIR: Training and Portal
|
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Toxicology Community
|
Toxicology has been an active research field for many decades, with academic, industrial and government involvement. Modern omics and computational approaches are changing the field, from merely disease-specific observational models into target-specific predictive models. Traditionally, toxicology has strong links with other fields such as biology, chemistry, pharmacology and medicine. With the rise of synthetic and new engineered materials, alongside ongoing prioritisation needs in chemical risk assessment for existing chemicals, early predictive evaluations are becoming of utmost importance to both scientific and regulatory purposes. The current main goal of the Toxicology Community is to support the integration of standards, tools and resources to support toxicology research projects and risk governance at the national and international level. Goals of the CommunityThe ELIXIR Toxicology Community was created in 2020. Its goals are: Align open solutions from toxicology research with ELIXIR services and resourcesBoth toxicology projects and ELIXIR Platforms and Communities have developed models, ontologies, educational material and standards. The Toxicology Community will align efforts and maximise the benefit. For example, various toxicology projects have been using Bioschemas annotation in online training material. Connect toxicology research with ELIXIR Platforms and CommunitiesMore synergy can be found by more closely connecting the core ELIXIR resources and communities with the inclusive communities that have evolved over the past few years like OpenTox, eNanoMapper, diXa, OpenRiskNet, NORMAN and older communities like the Federation of European Toxicologists & European Societies of Toxicology (EUROTOX), the Society of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry (SETAC) and European Environmental Mutagenesis and Genomics Society (EEMGS, formerly known as EEMS). Develop open community standardsToxicology projects like OpenTox, diXa, eNanoMapper, and others have already developed various open, domain-specific standards. Some in collaboration with ELIXIR projects like bio.tools, FAIRsharing, etc. This goal aims to further develop open community standards to support common interest, including ontologies, APIs, data formats, deposition databases, and publication recommendations. Leadership
(ELIXIR Netherlands) 
(ELIXIR Netherlands) 
(ELIXIR France) 
katharina.heil@elixir-europe.org (Communities Liaison, ELIXIR Hub) Additional Community support
Find out more
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Train the Trainer (TtT) website
|
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Pellentesque porta, urna nec dapibus gravida, elit risus placerat eros, quis suscipit odio neque sit amet tortor. Quisque dapibus odio pharetra metus suscipit, id mattis augue molestie. In quis malesuada nisl, ac tincidunt justo. Integer sagittis purus. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Training bioinformaticians in High Performance Computing
|
Training bioinformaticians in High Performance Computing.Esteban Pérez-Wohlfeil, Oscar Torreno, Louisa J. Bellis, Pedro L. Fernandes, Brane Leskosek, Oswaldo Trelles. Heliyon 4 (2018) e01057. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TtT and Training impact workshop report
|
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TtT training materials GitHub repository
|
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tutorials for development of material for Galaxy
|
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. |



 (Opens a new window)
(Opens a new window)