Public services
| Name | Description | ELIXIR Node | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Data for Life podcast
|
ELIXIR's Data for Life podcast looks at the potential and current influence of data in medicine, genomics, biodiversity and many more life sciences. It features pioneers, entrepreneurs, investors and academics, who discuss the rapid growth of the bioinformatics industry, the factors steering the field towards success, and the importance of open science. Episodes include influential and innovative people in biodata in Europe, such as Maria Chatzou Dunford (Founder of Lifebit), Hans Garritzen (Sales Director at MediSapiens) and Abel Ureta Vidal (Founder of Eagle Genomics). The podcast is hosted by Hannes Rothe (Professor for Educational Service Engineering and IT Entrepreneurship, Freie Universität Berlin) and Katharina Lauer (Industry Officer, ELIXIR Hub). Learn more about the hosts. Previous episodes23 June 2021In the latest Data for Life podcast, Hannes and Kathi talk to Abel, a bioinformatician, serial entrepreneur, investor, mentor, and open science enthusiast. He has been living the Europe dream – a Spanish born, French-educated and British-inspired entrepreneur. Exploiting open research data, Abel built a thriving bioinformatics business. 4 February 2021How can studying history prepare you for a career in bioinformatics? Why has Finland become a hub for genomics ventures? What is the current state of data quality in the life sciences, and how does this affect ventures? In this episode, Kathi and Hannes will move to Europe’s North to find the answers to these pressing questions, with Hans Garritzen from Medisapiens. The Finnish company provides clients with a digital health platform to leverage big biomedical data from public and private domains. 25 November 2020Hannes and Kathi welcome Maria Chatzou, CEO and Co-Founder of drug discovery startup Lifebit to the first interview of the Innovation series. In this episode, they explore Cambridge, one of the most important ecosystems for biodata-centred businesses and unveil Maria’s experience in this competitive fast-moving industry — as both a successful bioinformatician and an entrepreneur. 15 October 2020Why is biodata essential now and why for everyone? Welcome to the Data for Life podcast, innovation series. Discover with Hannes Rothe and Kathi Lauer the world of biodata and its fruitful future for innovation. With the perspective of an entrepreneur and a virologist, you will be immersed in the innovative ocean of (open) life science data. About the hostsWhat do a medical scientist and an economist have in common?
Kathi Lauer, ELIXIR Industry officer and doctor in medical sciences, met Hannes Rothe, an economist and entrepreneur, in Berlin at an entrepreneurship event on Digital Startup Ecosystems in 2017. Since then, they have been working together to understand what drives businesses to succeed in the field of biodata.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data Management Coordinators
|
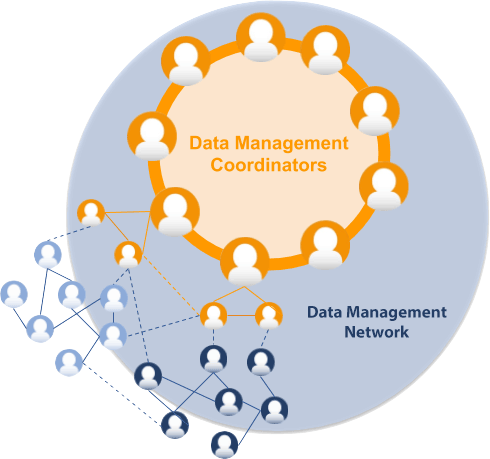 The ELIXIR Data Management Coordinators group consists of one or two appointed representatives from each ELIXIR Node. The Data Management Coordinators are the main contact points for each Node regarding Data Management issues. The Data Management Coordinators form the core of the ELIXIR Data Management Network. Its formation was a milestone in the ELIXIR-CONVERGE project (WP1), and its members help ensure the delivery of the expected outcomes of this project work package. To achieve this, the Data Management Coordinators will rely on members of the larger ELIXIR Data Management Network and resources in the different Nodes. The Data Management Network interacts through a mailing list, as well as through regular monthly meetings that are used for sharing of best practices, and how Data Management support is done in different countries. It is expected that the Data Management Coordinators will continue as a function of ELIXIR after the completion of ELIXIR-CONVERGE. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data Management Network
|
 The ELIXIR Data Management Network group brings together the Data Management community across ELIXIR. If you are interested in Data Management, it is a way you can communicate and share ideas across all the ELIXIR Nodes. The group has been established as an outcome of the ELIXIR-CONVERGE project. The core of the Data Management Network is the Data Management Coordinators group. This group is made of Node representatives, who rely on the wider Data Management Network to deliver the outcomes of ELIXIR-CONVERGE. The Data Management Network interacts through a mailing list, as well as through regular monthly meetings. These are used for sharing best practices and for discussing how Data Management support is done in different countries. The group is open to join for anyone interested in Life Science Data Management issues. If you belong to an ELIXIR Node and you are interested in Data Management, you are strongly encouraged to join! |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Director
|

ELIXIR Director The ELIXIR Director is responsible for implementing the decisions of the ELIXIR Board. The Director:
The current ELIXIR Director is Tim Hubbard. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Domestic Animals Genome and Phenome Focus Group
|
This Focus Group supports genotype to phenotype analysis for farmed and companion animal species. Connecting researchers and data scientists across species and countries is needed to accelerate genotype to phenotype research in domestic animals, and develop a coordinated, open and standardised data life cycle. We aim to develop the case for a future Community and make initial progress at promoting and aligning tools, databases, standards, and best practices for domestic animal genomics and phenomics research. Goals
Leadership
(ELIXIR UK) 
(ELIXIR Netherlands) 
(EMBL) 
(ELIXIR France) 
(ELIXIR Hub Liaison) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELITMa: ELIXIR Training in Management
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR All Hands
|
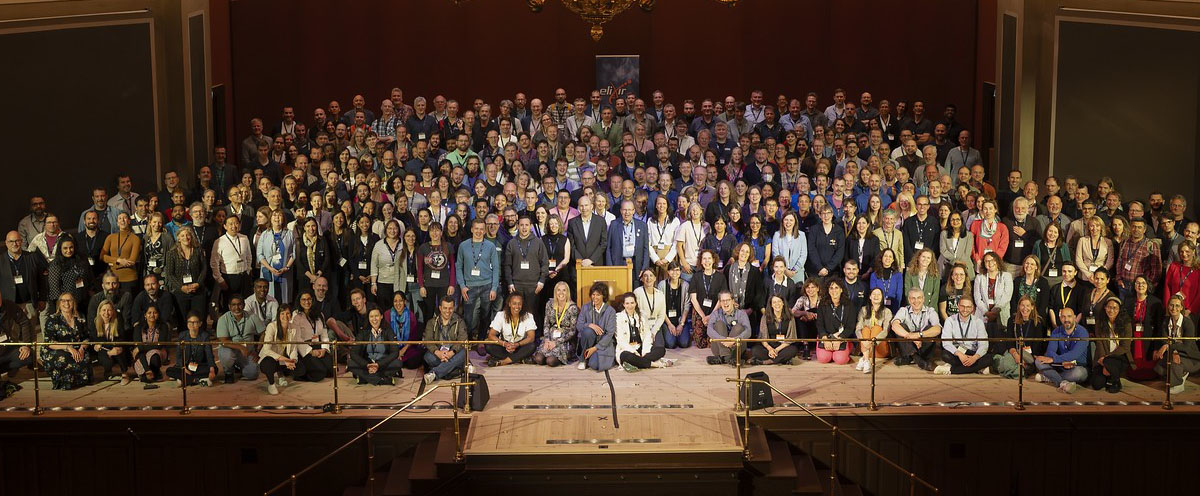

The ELIXIR All Hands meeting is an annual event that brings together members of the ELIXIR community. The goal of the event is to review ELIXIR’s achievements and activities so far, and discuss plans for the future. It includes:
The All Hands event usually takes place in June and is for ELIXIR members and invited guests only. All Hands 2025The 11th ELIXIR All Hands meeting will take place from 2 to 5 June 2025 in Thessaloníki, Greece. For detailed information, please see our event page or the event website for full details. Previous All Hands meetingsVideos of presentations are available for the 2020 meeting. Other meetings have links to presentation slides and photographs.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR Board
|
The ELIXIR Board is the decision-making body in ELIXIR. The Board consist of scientific and administrative representatives from each ELIXIR Member State and EMBL. Members of the Board are authorised to deliberate, negotiate and decide on behalf of the respective Members. What the Board doesThe Board's powers are defined in the ELIXIR Consortium Agreement. Among other responsibilities, the Board:
Members of the Board
ObserversIn addition, countries working towards signing the ECA have appointed representatives to the ELIXIR Board as Observers.
ELIXIR Board, April 2024 – Hinxton, UK |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR Collaboration Agreement
|
The ELIXIR Collaboration Agreement is the legal document that grants the status of an ELIXIR Node to a national community in an ELIXIR member state. It ties together the ELIXIR Hub with the national Node, establishing general responsibilities, a baseline governance structure and oversight of Node services. It enables the ELIXIR Hub to commission services (i.e. Commissioned Services) to ELIXIR Nodes and establishes framework conditions for the funding, with further details defined in separate funding agreements (i.e. Proposals of Funding). The ELIXIR Board approved the original Collaboration Agreement template in 2014, which has since been revised. The updated version of this template, i.e. Collaboration Agreement 2024 template, is currently in use. Please contact legal@elixir-europe.org if you wish to request a copy of the Collaboration Agreement template 2024. The Collaboration Agreement includes two Annexes:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR Node Industry Engagement Days Pilot Programme (2023)
|
Open call: 1 February to 31 April. See the call details.
Companies will have the chance to learn more about ELIXIR services and to forge strong links with the local ELIXIR representatives running these services, and consider building collaborative projects. This scheme gives the opportunity to Nodes to explore the relevant national landscape, and define the Node’s motivation and focus for building an industry engagement strategy aligned with the Node’s strategic goals and priorities. This scheme covers the costs of the venue, catering, travel expenses and salary costs up to a maximum of 1/2 person month per project. See the detailed information about the 2023 Open call for how to apply. Benefits of hosting an Industry Day
What could follow-up after the event
Relevant document: How to Engage with Industry |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR support for biodiversity research
|
ELIXIR Nodes provide services that you can use to support biodiversity research. These include: analysing, annotating and archiving DNA sequence and other molecular data; finding and annotating biodiversity-relevant data; linking and integrating data sets, and many others. The page below provides further information, it will be updated frequently, any questions please contact Physilia Chua (Physilia.chua@elixir-europe.org).
Archive DNA data in the correct repositorySequence-based approaches to address biodiversity questions are now widely used and diverse. They can range from the generation of full annotated genomes to short sequence markers. These data can be used to address questions around taxonomies, species occurrence, dietary make-up, species abundance, and many others. As an open data infrastructure, we encourage you to deposit all raw and consensus DNA sequence data in the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA). If you are not sure how to use the ENA then take the free online course. It takes about 30 minutes to complete. Wider assitance and guidance to help with data management, can also be found in the ELIXIR RDM Kit, an online guide containing good data management practices applicable to research projects from the beginning to the end. Access and retrieve data relevant to biodiversityELIXIR provides a range of data resources that allow scientists to access and retrieve Biodiversity relevant data of various types:
Make your data easier to find and share (FAIR)ELIXIR has an extenisve set of services that can help in making Biodiversity data sets more FAIR, including:
Find software and workflows to analyse your dataELIXIR provides a diverse range of Services that can assist in the analysis of Biodiversity data:
Find computing resources to help you analyse datasetsELIXIR Nodes run computing services that can be accessed by research projects. Many additional computing resources have been made available to support a range of research projects and a number offer access to Docker Orchestrators including Mesos and OpenStack access, Kubernetes/OKD and potentially GPUs where needed - for assistance please contact jonathan.tedds@elixir-europe.org, ELIXIR’s Compute Platform Coordinator. Specific examples of compute resources include:
Find training materials to help you get startedUse the ELIXIR Training Portal TeSS to find training courses and materials for hundreds of Bioinformatics Tools and Services. Contribute to ELIXIR’s Biodiversity workJoin the ELIXIR Biodiversity Community. Additional key Services, not part of the ELIXIR InfrastructureThe work of the ELIXIR Biodiversity Focus Group has identified a number of key services that are highlighted below, which are not currently part of the ELIXIR infrastructure, but which are highly relevant: COPO - COPO is a data brokering service to help describe, store and retrieve genomic data more easily, using community standards and public repositories. For instance, DNA sequence data can be deposited in the ENA more easily using the standards and processes set out by COPO. GlobalFungi - global repository of fungal metagenomic data obtained by next-generation-sequencing shared through a web based interface that allows various queries of the database and visualization of the results. The database covers data from all terrestrial habitats except those subject to experimental manipulation, containing information on fungal communities from soil, litter, dead plant material, living plant tissues and others. Treatmentbank - Search the Plazi resource Treatmentbank using fulltext search or taxonomic names, bibliographic records or observation records to retrieve rich data about described species. Biodiversity Literature Repository is a community in Zenodo providing FAIR data liberated from taxonomic publications, that is taxonomic treatments, figures and annotated deposits of publications. It is the repository of the TreatmentBank service. SIBiLS - Triage the literature with SIBiLS, which has pre-annotated the literature (MEDLINE, PMC, Treatmentbank, Allen AI pre-prints, ...) with a broad range of ontologies (taxonomic names, biotic interactions, ...). SIBiLS is a back office curation-support service and several of its annotations are mirrored into EuropePMC. Other European-based biodiversity-relevant infrastructuresELIXIR is part of a much wider network of Infrastructures dedicated to Biodiversity and with whom ELIXIR collaborate.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR webinar guidelines
|
IntroductionA webinar is a live presentation by one or more speakers and open to all. The presentation will last 30-45 minutes followed by Q&A. The registration link will be promoted through ELIXIR channels and others. The presentation will be recorded and made available on YouTube.
Purpose of a webinar
Planning a webinarIf / when the idea is first raised please complete this form. The more details the better, but everything can be discussed before the event is published.
Technical requirements
Promotion (ELIXIR Hub)
Before the event (ELIXIR Hub)
On the day
Afterwards (hub)
Considerations
Examples of Webinars include:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-CONVERGE WP9: Mobilisation of SARS-CoV-2 variant surveillance data tracking services and tools
|
The European COVID-19 Data Platform enables the collection and sharing of research data for the European and global research communities. Data mobilisation is a core role for the Platform: via the SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs viral raw sequence and assembled genomes can be systematically processed, openly shared, and variants examined in a wide ecosystem of visualisation and phylogenetic analysis tools. The objective of this work-package is to mobilise viral genomes from national sequencing efforts in Europe and beyond into truly open data resources for surveillance of COVID-19 variants and expose variation data rapidly for analysis. This will be achieved by linking nascent and established national sequencing efforts to the COVID-19 Data Platform by setting up submission and annotation pipelines to the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA). Participating efforts will commit to open sharing of variant data through ENA. Objectives
TasksTask 9.1 Strengthen central Covid-19 Data Portal help desk for individual centres and brokersSubtask 9.1.1 Strengthen central SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs Help Desk for easier and improved data submission into the European COVID-19 Data Platform for scalability This subtask will ensure appropriate availability of data and tools from the COVID-19 Portal from EU research projects in which EMBL-EBI is a partner (other than VEO and ReCoDID, as these are covered in their respective projects). These projects include (aligned EU projects shown in italics):
Subtask 9.1.2 Provide supported SARS-CoV-2 data brokering interfaces for external data platforms: The national/regional SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs offer a broad portfolio of tools, from simple intuitive "drag and drop" web pages to RESTful APIs. We will extend these tools to reflect the emerging needs of the SARS-CoV-2 data brokering community. To provide clear and efficient data routing for all data providers, we will coordinate across sub-tasks 9.1.1 and 9.1.2 to ensure that countries and laboratories have a single service provider for their data, be this direct (subtask 9.1.1) or via brokering (subtask 9.1.2). Leadership: EMBL-EBI Task 9.2 Coordinate nascent and established national data hubs focusing on brokering services to mobilise data and define and foster common best practicesSubtask 9.2.1 Coordinate nascent and established regional/national data hubs: This task will engage national SARS-CoV-2 data hubs and support software engineering and curation resources at each centre, to establish a network of open data submission pipelines. It will bring together resource managers in charge of the regional/national SARS-CoV-2 data hubs to share expertise, tools and define common best practices for capacity building and harmonised approaches. This will make sure that hubs share tools/code as much as possible to avoid redundancies, and also that the data standards adopted in Task 9.3 are well implemented across the national hubs. This network will also enable discussions on the open data policies undertaken in each country and support sharing of experience to encourage countries to support/require ENA data submission in addition to GISAID. The network will also discuss how the open source tools can be adaptable to genomics surveillance beyond SARS-CoV-2, in a One-health approach. The network will work to ensure that data flows between stakeholders' platforms, to build together a globally comprehensive set of viral sequence and variation. Subtask 9.2.2 Establish dedicated user support and capacity building for viral data management and submission: This task will open up already established national tools for broad use across European member states, and provide training and capacity building for countries and institutes that are now rapidly scaling up their efforts. Robust platforms are already in operation in many ELIXIR Nodes provide foundations for this work. For example, SIB (CH) has developed the Swiss Pathogen Surveillance Platform (SPSP.ch) and ELIXIR-BE (in collaboration with others) has developed a Galaxy-based submission system, as well as the underlying command-line tools. Further developments to submit consensus sequences to ENA as well as to GISAID will be developed. Methods to submit variant data to EVA will be explored and integrated. Brokering functions operated by these platforms will be supported. Use-case based documentation to disseminate the submission tools and best practices will be integrated into the RDMKit. This targeted approach complements the available information in the COVID19 Data Portal. Leadership: SIB/ELIXIR-CH Task 9.3 SARS-CoV-2 data standardsSubtask 9.3.1 Variation calling and variant lineage nomenclature standards: In this subtask, we will establish standards and best practices for variant calling, naming, observation and citation. To achieve this, we will engage key players in viral lineage analysis and naming (e.g. Pangolin, Nextstrain, WHO) to drive harmonisation and establish authoritative naming schemes. Subtask 9.3.2 Ontologies and controlled vocabularies for metadata: National and regional hubs are collecting metadata in various forms. These metadata are then submitted to the ENA using the ERC000033 checklist that has both compulsory and recommended fields. Many of the fields of this minimum metadata standards are currently free text. These data are however likely to be stored in a structured form at local hubs, using ontologies and controlled vocabularies. In this subtask, the need for using ontologies and controlled vocabularies will be discussed and best practices recommendations will be outlined and shared within the network established in Task 9.2. Leadership: UKZN/South Africa Task 9.4 SARS-CoV-2 AnalysisSubtask 9.4.1 Adoption of VEO (Versatile Emerging Disease Observatory) variant and lineage analysis tools into the portal: Supporting work in VEO WP16, we will provide compute capacity and an appropriate workflow engine, integrated in the Data Hubs, to accommodate the evolving and new analytical workflows that emerge. We will provide appropriate adaptation and configuration of these workflows and make available the global viral data content to these. These workflows will generate processed data that will be integrated in the COVID19 Data Portal, ensuring common analyses across all data. Expected work will include the hosting of high-throughput phylogenetics tools, a reference implementation of lineage naming, tools to link variation to variants and country report generation tools Substask 9.4.2 COVID-19 Data Portal data access and analysis: This subtask aims to enable data analysis for all researchers across Europe and globally, irrespective of the availability of local computational infrastructure. We will provide a common environment through Galaxy to enable analysis for all global stakeholders. We will integrate existing, relevant workflows, including the workflows used within the SARS-CoV-2 Data Hubs. We will ensure relevant data is readily available in the platform, through automatic procedures integrated with the European COVID-19 Data Portal through, for example, APIs or FTP. Synchronising the data, combined with the mobilisation of data in this WP, allows the development of monitoring services and visualisations. Relevant visualisations can be integrated in Galaxy through regular (static) visualisation tools, interactive Galaxy tools or through integration with external services e.g. viral Beacons, Nextstrain. The workflows will be made available on public servers (e.g. https://usegalaxy.eu), as well as for local deployment (e.g. through containers). All code developed will be available under Open Source licenses.Substask 9.4.3 Dissemination and capacity building An important aspect of Task 9.4 is training of researchers and support personnel to use the workflows and resources for data analysis and sharing. The training in data submission is covered in Task 9.2. Through hackathons, we will engage with the broader community to develop and implement workflows, data access tools and features of Galaxy. These dissemination efforts will build on the Galaxy Training Network and the online course materials that have been developed in recent months. Leadership: ALU-FR/ELIXIR-DE Deliverables
WP leaders
SIB 
UiT 
ISCIII 
UiT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-funded activities
|
Commissioned Services and Capacity Building and Knowledge Exchange programmeELIXIR funds activities that connect and integrate services across ELIXIR Nodes. These projects are led by experts from specific Platforms or Communities, leveraging national strengths and facilitating collaboration and integration across ELIXIR Nodes. There are two types of ELIXIR-funded activities:
Commissioned ServicesCommissioned Services are projects funded through ELIXIR's own budget. They’re projects that:
The current Commissioned Services projects align with ELIXIR's 2024–28 Scientific Programme priorities: Science, Technology, People and Nodes. Click on the links below to discover more about the Commissioned Services projects for each priority.
Capacity Building and Knowledge Exchange programmeThese funding opportunities strengthen the links between and facilitate capacity building in ELIXIR Nodes, as well as supporting the exchange of best practices in bioinformatics service provision. They include Staff Exchanges, Travel Grants, Knowledge Exchanges and Industry days. Calls now openCapacity Building and Knowledge Exchange programmeFind out how to apply for funding for Staff Exchanges, Travel Grants, Knowledge Exchanges and Industry days.Find out more
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS
|
 ELIXIR-STEERS aims to help life science researchers to access national data sets and conduct large-scale, cross-border analysis of data from across Europe. It will promote good software management practices and support life scientists with their software management needs. It will collect these good practices into a toolkit for green and reproducible software and workflows. BackgroundELIXIR STEERS builds on the work of two previous European projects:
ObjectivesELIXIR STEERS ensures that ELIXIR continues to operate as a world-class Research Infrastructure (RI), and continues to enable wider participation in computational life science research. It will focus on a new and critical area of scientific need: the provision of software and workflows to life scientists, maximising productivity in research, and minimising consequent energy usage. It will:
Work Packages and their leaders
Participants38 research institutes in 25 countries across Europe. DeliverablesThere are 17 deliverables. See the deliverables page. GovernanceThe project is coordinated by the ELIXIR Director (at the ELIXIR Hub). It is overseen by the Management Board, which is made up of the STEERS Work Package leaders and the ELIXIR Director. The Board receives input from the ELIXIR Heads of Nodes Committee, the ELIXIR Scientific Advisory Board, and the ELIXIR Industry Advisory Committee. For more about these advisory bodies and how ELIXIR is run see Governance. Principal Investigator
Interim Director of ELIXIR and Head of External Relations (ELIXIR Hub) DurationThree years (February 2024 - January 2027) Budget€4M Contact |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS deliverables
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS participants
|
The ELIXIR-STEERS project involves 36 institutes in 23 countries.  |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS WP1: Coordination and support
|
This WP will oversee the project execution and ensure the project goals are accomplished within the expected scope, timeframe, and resources, and with the required level of quality. It will also monitor the risk, issues, and opportunities to maximise the benefit delivered by the project. Objectives
TasksTask 1.1 Project mobilisation and guidance - adoption of project management boards, governance and internal project communicationThe management structure proposed for ELIXIR-STEERS is based on the current governance structure of ELIXIR which has proven to be valued in the previous EC project (ELIXIR-EXCELERATE and ELIXIR-CONVERGE). The project will benefit from the fact that we are using governance bodies already in place with extensive experience in EC grants, minimising the time required to mobilise the project. Deputies will be named in all governance and management bodies with diversity, geographical location and gender balance considered when defining the composition of the boards. ELIXIR will act as coordinator and chair of the General Assembly (GA) (composed of representatives of all project beneficiaries that have delegated the decision making to the ELIXIR Heads of Nodes (HoN)) and the Management Board (MB: Coordinator + WP Leaders + Project Manager). ELIXIR’s existing independent Scientific Advisory Board and Industry Advisory Committee will be used to provide external governance reviews on project activities. While the MB will be responsible for the implementation of any decision affecting the description of action or resource allocation, it will have to be approved by the GA. Goals and responsibilities for each board will be formalised through the consortium agreement and detailed in the Project Handbook. The Project Handbook will also include the internal communication plan and procedures. Leadership: Juan Arenas and Nikki Coutts (ELIXIR Hub) Participants: All partners will contribute to this task. Task 1.2 Project monitoring and supportThis task comprises the execution of the project plan in collaboration with the project boards, WP leaders and the project participants. All monitoring and control activities (technical, financial, KPIs, risk, issues, quality assurance, change management) will be carried out as defined in the Project Handbook. Monitoring and control activities will require input from all participants and will be reported every six months at the participant, WP, and project level. This WP is also responsible for the organisation of all project meetings: GA, MB, Board Meetings and EC Review Meetings. The WP specific meetings will be the responsibility of the WP leaders and the project partners active in each WP. Project closure is also included in this task. Leadership: Juan Arenas and Nikki Coutts (ELIXIR Hub) Participants: All partners will contribute to this task. Task 1.3 Development and implementation of a project data management plan and correlated activitiesThe project data management plan (DMP) will be delivered early in the project. This will build on EC Horizon Europe requirements and recommendations as well as the ELIXIR position paper on FAIR data management. Ethical and legal compliance measures will be considered when developing the DMP and it will be updated on a regular basis to capture the relevant changes. The FAIR compliant DMP will incorporate relevant project components from each WP, while taking necessary restrictions into account. External projects using project results will have their own DMP. Leadership: Juan Arenas and Nikki Coutts (ELIXIR Hub) Participants: All partners are expected to contribute to the incremental versions of the DMP. Task 1.4 Development of long-term sustainability plan for project outputsSustainability of project results will be sought to ensure impact is maximised. Individual project outputs will be identified and evaluated to select the best approach for ensuring their sustainability considering the IP of project partners. It is expected that project results comprising methods, guidelines, standards, training, and tools will be made accessible though ELIXIR related services and platforms and open licences will be adopted (e.g., CC BY). To ensure proper management of sustainable outputs, a specific section will be included in the MB standing agenda (where all WPs are represented) to enable the early identification of project results and an individual sustainability pathway proposal. Leadership: Juan Arenas and Nikki Coutts (ELIXIR Hub) Participants: All partners will contribute to this task. Task 1.5 Excellence in ManagementIn collaboration with WP4, we will continue to build capacity in management across our ELIXIR Nodes.
In addition, we will continue to implement the ELIXIR Equal Opportunities Strategy and create a framework for adopting and strengthening the EC's Horizon Europe Gender Equality Plan (part of the EC Gender Equality Strategy 2020-2025) within an organisation which can then be reused by the ELIXIR Nodes. This work will link to 'B4W - ELIXIR LEadership And Diversity mentoring programme - ELEAD Pilot', an ELIXIR Strategic Implementation Study which is due to start in June 2023. As part of excellence in technical coordination, the ELIXIR Hub team will work closely with WP2-WP5 to promote adoption of the outputs generated at the European (e.g., via ELIXIR Nodes and EC projects) and international level (e.g., via the ELIXIR & GA4GH collaboration). Leadership: Laura Carletti, Juan Arenas and Nikki Coutts (ELIXIR Hub), Alba Jene, Eva Alloza (BSC, ES) Participants: All partners will contribute to this task. WP leaders
ELIXIR Hub 
ELIXIR Hub 
ELIXIR Hub |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS WP3: Infrastructure services to enable adoption and deployment of software best practices
|
WP3 will extend existing infrastructure components to implement the best-practices and indicators for research software and workflows developed in WP2. To ensure adoption of the best practices and aid recognition of the indicators, WP3 will integrate relevant features in community-adopted and recommended registries, and expose them in platforms used for assessing research outputs. Further dissemination of these practices will be done through the development of a Software Management Planning tool, with integrated guidelines. To stimulate reproducible analysis methodologies and raise the awareness of the environmental impact computational data analysis has, we will focus on benchmarking common analyses of the ELIXIR Communities. To make optimisations readily available for researchers, we will implement new features in workflow management systems. By leveraging commonly used technologies and platforms, we will contribute to a more sustainable ecosystem for computational analysis.Objectives
TasksTask 3.1 Enable crediting scientists for research assetsIn this task, we will build upon existing platforms and services (e.g., APICURON, ORCID, BIP! Scholar) that empower scientists to be credited for research assets and activities beyond publications. Our focus will be on delivering new or improved features related to software, tools, and workflows, to expose the credit information in relevant software and workflow registries (e.g. bio.tools, WorkflowHub). This will be achieved through enabling interoperability of the aforementioned platforms and services, and open Science Knowledge Graphs (e.g. the OpenAIRE Research Graph) using schema.org (Bioschemas) markup. Leadership: Thanasis Vergoulis (ATHENA RC), Damiano Piovesan (University of Padua), Veit Schwämmle (University of Southern Denmark), Lars Juhl Jensen (University of Copenhagen), Olivier Sallou (University of Rennes), Henning Hermjakob (EMBL-EBI), Balazs Gyorffy (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Carole Goble (University of Manchester), Salvador Capella-Gutierrez and Laura Portell-Silva (BSC). Task 3.2 Contributing towards sustainable research software through Software Management PlansWe will develop new features in the Data Stewardship Wizard (DSW) to enable the generation of Software Management Plans (SMPs), based on input from WP2. We will align with T3.1 and build on the work of ELIXIR and RDA to implement the guidelines and best practices for software development in research and infrastructure projects. As part of the process, engagement with relevant industry users of ELIXIR will provide additional insights to both the content and interface of the SMP. For ML-based software, we will build on the work of the ELIXIR Machine Learning Focus Group e.g. the DOME recommendation, and the integration with bio.tools. Also, new integration services and resources will be created to support researchers in composing and using a SMP e.g. to retrieve information from code repositories. We will disseminate the best practices, integrated in DSW, to both academia and industry, in collaboration with WP5. Leadership: Marek Suchánek and Jan Slifka (UOCHB), Mark Ibberson and Vassilios Ioannidis (SIB), Frederik Coppens (VIB), Salvador Capella-Gutierrez and Laura Portell-Silva (BSC), Yvonne Kallberg (Stockholm University), Veit Schwämmle (University of Southern Denmark). Task 3.3 Identify fit-for-purpose reproducible workflows through technical and scientific benchmarkingIn this task, we will extend the OpenEBench community-led evaluation feature, enabling the benchmarking of workflows used for common analyses in the life sciences. The workflows will be identified in collaboration with WP2 and the ELIXIR Communities. The evaluation will be based on community agreed indicators (defined in T2.2), covering both technical and scientific aspects, with a specific focus to enable assessment of impact and usage of software, e.g., energy consumption and physical resources needed, algorithmic and data effectiveness, as well as the recognition received by its developers and users. We will engage with industry (with WP5) e.g. to explore (energy) optimised infrastructure for specific computational jobs. We will also consider relevant practices and techniques from the TIER2 (HORIZON-WIDERA-2022-ERA-01-41) project like the badging approaches. The results will be exposed as FAIR Digital Objects represented as Workflow-RO-Crates using Bioschemas workflow markup as developed in the EOSC-Life Cluster project and ESG project (HORIZON-INFRA-2021-EOSC-01-04). These will be integrated in WorkflowHub for reproducibility and dissemination to end-users, both in academia and industry. Leadership: Laura Portell-Silva and Salvador Capella-Gutierrez (BSC), Carole Goble (University of Manchester), Thanasis Vergoulis (ATHENA RC), Wei Gu (PNED), Marco Tangaro (CNR), Mark Ibberson and Vassilios Ioannidis (SIB), Wolmar Nyberg Åkerström (Uppsala University), Ana Portugal Melo (biodata.pt), Veit Schwämmle (University of Southern Denmark), Dan Ben-Avraham (Weizmann Institute of Science), Kjell Peterson, (University of Bergen), Espen Robertsen (UiT The Arctic university of Norway), Brane Leskošek (University of Ljubljana). Task 3.4 Integrating optimisation criteria for environmental impact in commonly used workflow management systemsBuilding upon commonly-used technologies and workflow management systems (WMSs e.g. Galaxy, Nextflow) we will deliver features that make researchers aware of the environmental impact of an analysis, and enable them to take it into account. Our approach will be three-fold:
Leadership: Nicola Soranzo (Earlham), Björn Grüning (University of Freiburg), Thanasis Vergoulis (ATHENA RC), Lukas Hejtmanek, (UOCHB), Alexander Kanitz (SIB), Juha Törnroos (CSC), Marco Tangaro (CNR), Frederik Coppens (VIB), Anthony Bretaudeau (INRAE), Hedi Peterson (University of Tartu) WP leaders
ELIXIR Belgium 
ELIXIR Spain |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ELIXIR-STEERS WP4: Strengthening and equipping ELIXIR Nodes and Node staff with key skills and resources in organisation, management and training
|
The overall goal of this WP is to strengthen the organisational, managerial, and training skills of ELIXIR Nodes, thus enabling their effective operation. Effective operations will lead to more efficient, more visible, and widely accessible services, in addition to increased performance of ELIXIR as a pan-European RI. Objectives
TasksTask 4.1 Embedding good practices in ELIXIR Node OperationsELIXIR Nodes need to make themselves sustainable by embedding good practices. Task 4.1 aims to lay the groundwork for this goal by:
Leadership: Jiří Vondrášek, Anna Strachotova and Natalia Pizemova (UOCHB), Celia van Gelder and Mijke Jetten (Health-RI), Wei Gu (PNED), Gyorffy Balazs and Zsuzsanna Dosztanyi (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Brane Leskošek (University of Ljubljana), Franscesca De Leo (CNR), Martin Reczko (BSRCAF), Bengt Persson, Jessica Lindvall and Jessica Lindberg (Uppsala University), Hedi Peterson, (University of Tartu), Dan Ben-Avraham (Weizmann Institute of Science), Ana Freitas (biodata.pt), Colm Ryan (University College Dublin), Fran Borovecki (University of Zagreb School of Medicine). Task 4.2 Organisational and research management capacity for NodesThis task provide ELIXIR Node staff with expertise in managing their operations. It builds on ELIXIR-CONVERGE efforts towards excellence in management, EMMRI masters courses delivered under RITrain and RITrain Plus, and complements ELIXIR's ongoing efforts to develop its capacity in impact evaluation and outreach to funders.
These efforts can be adapted to the context of other RIs and contribute to the overall strengthening of the ESFRI landscape. Leadership: Ana Freitas (biodata.pt), Anna Strachotova (UOCHB), David Dolan (University of Bergen), Bengt Persson (Uppsala University), Celia van Gelder, Mijke Jetten (Health-RI), Wei Gu (PNED), Brane Leskošek (University of Ljubljana), Lucy Poveda (SIB), Balázs Győrffy, (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Munazah Andrabi (University of Manchester), Xénia Perez (Earlham Institute), Dan Ben-Avraham (Weizmann Institute of Science), Hedi Peterson (University of Tartu), Fran Borovečki (University of Zagreb School of Medicine), Colm Ryan (University College Dublin). Task 4.3 Capacity building in training skills for ELIXIR Node staffThe task aims to build training capacity in ELIXIR Node staff, targeting those with technical and training roles. Training knowledge and skills implemented in the Nodes will enable the RI to promote their expertise and work more efficiently. The task builds upon already established good practices and resources within the ELIXIR Training Platform (e.g. the ELIXIR-GOBLET Train-the-Trainer programme) and within the Nodes (e.g. training courses and materials), and will also leverage knowledge in resources connected to ELIXIR such as GOBLET (mygoblet.org), Intersect (intersect-training.org) and others. The task will:
Leadership: Erik Hjerde (UiT The Arctic university of Norway), Brane Leskošek (University of Ljubljana), Björn Grüning (University of Freiburg - Albert-Ludwigs-Universität), Patricia Palagi (SIB), David Dolan (University of Bergen), Eva Alloza (BSC), Colm Ryan (University College Dublin), Jessica Lindvall (Stockholm University), Zsuzsanna Dosztanyi (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Munazah Andrabi (University of Manchester), Jiří Vondrášek (UOCHB), Hedi Peterson (University of Tartu), Fran Borovečki (University of Zagreb School of Medicine), Ana Freitas (biodata.pt). WP leaders
ELIXIR Sweden 
ELIXIR Czech 
ELIXIR Portugal |
 Innovation in life sciences data is their common denominator. It has inspired them to join forces and create this exciting podcast. Yet, this is not the only outcome of their collaboration. Data for Life is part of a larger project to update the ELIXIR report on ‘
Innovation in life sciences data is their common denominator. It has inspired them to join forces and create this exciting podcast. Yet, this is not the only outcome of their collaboration. Data for Life is part of a larger project to update the ELIXIR report on ‘ Empowering ELIXIR staff members
Empowering ELIXIR staff members
 In order to support ELIXIR's industry and innovation programme, the ELIXIR Hub is encouraging the Nodes to host Industry engagement days with the aim to connect with the national industry ecosystem and boost the open innovation ecosystem in the life sciences in the country.
In order to support ELIXIR's industry and innovation programme, the ELIXIR Hub is encouraging the Nodes to host Industry engagement days with the aim to connect with the national industry ecosystem and boost the open innovation ecosystem in the life sciences in the country. 
