Public services
| Name | Description | ELIXIR Node | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
WP2: Implementation of research software best practices through ELIXIR Communities
|
The goal of this WP is to provide a collection of best practices and indicators for research software and workflows. To do this, the WP will engage with the 15 ELIXIR Communities, which will also provide use cases for the best practices. WP2 is linked with the services and infrastructure developed in WP3, which will capture Community input to steer development and drive adoption of best practices. WP4, which is about capacity building and training, will ensure ensure expertise/content from WP2 is disseminated across ELIXIR Nodes. WP2 will also provide support for the industry and scientific outreach activities in WP5. Objectives
TasksTask 2.1 Building the technical toolkit for software best-practicesThe objective of this task is to implement the technical toolkit by building a compendium of best practices for quality, sustainability, and impact of research software and workflows in life sciences. These best-practices will be used towards the definition of high-level processes (e.g. efficiency benchmarking, workflow optimisation). The task will be centred on developing the best-practices through a dialogue with technical stakeholders from relevant Communities (cf. Task 2.3) and is tightly linked with WP3, shaping service requirements, and adopting their technical solutions. The task will also address:
Leadership: Silvio Tosatto (University of Padua), John Hancock (University of Ljubljana), Fotis Psomopoulos (CERTH) Task 2.2 Identifying efficiency indicators for research software and workflowsThe objective of this task is to identify indicators for evaluating the efficiency, quality, environmental sustainability, and scientific impact of research software in life sciences. This will provide a basis for measuring the performance and usefulness of research software and will help stakeholders to make decisions about the sustainable development and use of such software. Activities of this Task include defining and implementing a set of indicators to assess the impact and usage of software, as well as the recognition received by its developers and users. The metrics used for this purpose will be aligned with the best-practices compendium (cf. Task 2.1). In close collaboration with WP3 and the different communities (cf. Task 2.3), technical benchmarking will be carried out, including defining relevant performance and functional requirements and assessing software capabilities against them.Finally, the task aims to identify indicators for algorithmic and data effectiveness, for further implementation in WP3 (cf. Tasks 3.3 and 3.4). The identified indicators will contribute to the technical toolkit (see D2.2). Leadership: Fotis Psomopoulos (CERTH), Salvador Capella-Gutierrez and Laura Portell-Silva (BSC), Silvio Tosatto (University of Padua), Karel Berka and Radka Svobodova (UOCHB), Zsuzsanna Dosztányi (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Fran Borovecki (University of Zagreb School of Medicine), Nanjiang Shu (Uppsala University), Artemis Hatzigeorgiou (Hellenic Pasteur Institute), George Spyrou (Cyprus Institute of Neurology & Genetics), Dan Ben-Avraham (Weizmann Institute of Science). Task 2.3 Adoption of best practices through Community engagementThis task will engage with existing and emerging ELIXIR Communities as well as communities linked to ELIXIR to:
This task will engage ELIXIR Communities with the work of Tasks 2.1 and 2.2. To this end, the Task will create a Community Engagement Dashboard capturing key indicators for involvement. It will organise online meetings and hackathons to engage people and to showcase its recommendations. Some of these meeting will include participants from industry. Leadership: John Hancock, Brane Leskošek and Polonca Ferk (University of Ljubljana), Silvio Tosatto and Damiano Piovesan (University of Padua), Fotis Psomopoulos (CERTH), Zsuzsanna Dosztányi (HUN-REN Research Centre for Natural Sciences), Henning Hermjakob (EMBL-EBI), Mijke Jetten (Health-RI), Karel Berka and Radka Svobodova (UOCHB), Anne-Francoise Adam-Blondon (INRAE), Jose María Carazo (CNB-CSICS), Lucy Poveda (SIB), Fran Borovecki (University of Zagreb School of Medicine), Vasilis Promponas (University of Cyprus), Dan Ben-Avraham (Weizmann Institute of Science). WP leaders
ELIXIR Italy 
ELIXIR Slovenia 
ELIXIR Greece |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3D-BioInfo Community webinar series
|
Uncovering new families and folds in the natural protein universeStructural bioinformatics provides methods and tools to analyse, predict, archive and validate the three-dimensional (3D) structure data of biomacromolecules such as proteins, RNA or DNA. The specific 3D shapes of macromolecules allow them to perform many functions within cells. Understanding their structures is therefore crucial for understanding the interactions and functions of cells, which in turn opens up potential for innovations in biotechnology and drug development. The 3D-BioInfo Community is concerned with improving the ontologies and validation tools for enabling better integration of the data and methods for analysing and predicting protein structures and their complexes. Part of this work is presented in an ongoing series of webinars:
FAIR Infrastructure for protein structural and functional annotations (3D-BioInfo Activity I)29 June 2021 15:00 CEST
Open Resources for sharing, integrating and benchmarking software tools for modelling the Interactome in 3D (3D-BioInfo Activity II)21 September 2021 15:00 CEST
Development of models for protein-ligand interactions (3D-BioInfo Activity III)19 October 2021 15:00 CEST
Protein Engineering15 February 2022 15:00 CEST
Assessment of large scale applications of Alphafold2 in structural bioinformatics
In Silico screen of protein-protein interactionsMachine learning for reconstructing dynamic protein structures from cryo-EM images
AlphaFold changes everything (and nothing)Addressing the void between protein sequence and structure
Cryo-EM and artificial intelligence: A marriage made in cellular fractions
Harnessing protein folding neural networks for peptide-protein docking: what have we learnedComputer Aided Drugs Design (CADD)
Causes and Consequences of Epistasis in Protein Evolution and Design
New Era of Structure Abundance - Insights into Protein Function14 October 2023 15:00 CEST
Is this yet another multiverse talk?! Exploring murky regions of the protein multiverse with ancestral fragments and deep generative models
SWISH-X, an expanded approach to detect cryptic pockets in proteins and at protein-protein interfaces Alberto Borsatto
EnquiriesPlease contact the Community Coordinator Katharina Heil (katharina.heil@elixir-europe.org). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
A new pan-European Train-the-Trainer programme for bioinformatics
|
A new pan-European Train-the-Trainer programme for bioinformatics: pilot results on feasibility, utility and sustainability of learning. Via A, Attwood TK, Fernandes PL, Morgan SL, Schneider MV, Palagi PM, Rustici G, Tractenberg RE. Brief Bioinform. 2019 Mar 22;20(2): 405-415. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accordion test
|
GDI Pillar I focuses on the operational planning for continuous high-quality services by addressing the long-term operational planning of national and European services. Pillar I provides the 1+MG Group and committed countries with models and frameworks on which they can agree to develop a sustainable, European genomics data infrastructure to support better healthcare and research. Pillar/WP leader: Regina Becker (PNED GIE), Elena María Doménech Cruz (INSTITUTO DE SALUD CARLOS III) Lead Partners: SIB (Switzerland), HITS (Germany), University of Padua (Italy) The objective of the ELIXIR Data Platform Executive Committee (ExCo) is to manage and coordinate activities throughout the 2024-2026 work plan, ensuring smooth operation and collaboration within the Platform.
Activity 1: Face-to-Face Meetings: Alternating between hosts and jointly with other PlatformsThis activity involves organising an annual face-to-face meeting for the ELIXIR Data Platform members in loose collaboration with one of the other ELIXIR Platforms. The meetings will rotate among the ExCo and their member states as hosts. The purpose of these meetings is to provide a dedicated platform for in-depth discussions, strategic planning, and decision-making. The ExCo will collaborate with the Hub to plan and execute the meeting effectively. The agenda will be designed to address key topics related to the Platform goals, initiatives, progress, challenges, and opportunities. The meeting will also provide a unique opportunity for Platform members to interact in person, fostering stronger working relationships and promoting a sense of unity within the Platform and across ELIXIR. The ExCo will ensure that the meeting outcomes are documented and disseminated. Activity 2: Monthly virtual meetingsThe monthly teleconferences (TC) or virtual meetings are a crucial element of the coordination and collaboration strategy of the ELIXIR Data Platform. These regular virtual meetings will provide a forum for effective communication, information exchange and activity among Platform members. The ExCo will oversee the scheduling of these TCs and develop an agenda for each. Lead Partners: EMBL-EBI (international organisation), VIB (Belgium) Activity 1: Landscape of data brokeringData brokering is the act of submitting data to one or more databases on behalf of another person/institute. It involves the coordination between data producers in an institution of an ELIXIR Node, which provides data management support, and deposition databases like the ELIXIR Deposition Database (EDD). Moreover, data producers might use Platforms or technical services (e.g. brokerage platforms) provided by the Node to collect and prepare (meta)data for publication into databases. Often, multi-omics studies would also require references among several datasets published in different databases to preserve the relations among data (data linkage). For any of these use cases, connections are based on data exchange formats and the mapping of metadata schemas. This task will build on and continue the work from the ELIXIR-CONVERGE project T1.2 on “Models for brokering data to ELIXIR Deposition Databases”, and in particular on multi-omics studies. The focus will be on the definition of “brokering” and landscape analysis of ELIXIR data resources and their existing requirements for data linkage and submission of multi-omics studies. Activity 2: Defining best practices for data brokeringData brokering can be done on different levels of operational complexity using different data exchange formats and metadata standards. In this task best practices and guidelines for data brokering will be defined to support repositories in developing or improving data submission and data linkage. Activity 3: Implementation use cases of best practicesThe implementation of best practices activity will build on the work of activity 2 (WP2.2) and the three data brokering scenarios analysed in the ELIXIR-CONVERGE project (WP1 T1.2), including the results from the BioHackathon 2022 project 27. The work will initially explore and further develop solutions based on the ISA abstract model and its implementation as ISA-JSON, which were used in ELIXIR-CONVERGE for brokering multi-omics studies. Then, the feasibility of extending the same approach to the other scenarios will be investigated. Following the work of activity 1 (WP2.1) and activity 2 (WP2.2), additional use cases will be selected to explore how the ISA-based solution can be expanded to support the proposed best practices for a wider range of domains/techniques and corresponding ELIXIR deposition databases. The activity will also evaluate a selection of complementary technologies (including RO-Crate) to develop a high-level technical proof of concept showcasing the feasibility and functionality of at least one of the representative use cases. WP3: Recognition and credit attribution of research contributions to data resourcesLead Partners: University of Padua (Italy) This WP will support the recognition and credit attribution of activities which curate, annotate or otherwise contribute to the increase of data in relevant resources such as knowledge bases. Further, it will leverage the work of APICURON to provide an infrastructural component to use in different contexts beyond more traditional biocuration activities (e.g. knowledge bases), ranging from ELIXIR registries (e.g. bio.tools, RDMkit, FAIR Cookbook, FAIRsharing), to code contributions (e.g. in GitHub) and data management/stewardship (e.g. data brokering). The resulting service will link the mapped data citations and credits for primary contributions to citation networks (e.g. OpenAIRE KG). Moreover, it will explore the possibility to generalise the approach and employ it in other contexts such as crediting trainers in Training Platform activities. In addition to the technological component, it will explore the “sociological” implications for the “person infrastructure”, including career pathways, fostering adoption and user engagement (e.g. with gamification techniques). Activity 1: Technical developments for recognitionThis task will continue the technical developments for implementing recognition and credit attribution mechanisms. The APICURON platform, currently restricted to curated databases, will be expanded to cover a wider range of activities, based on user input. On-boarding of additional ELIXIR resources will lead to technical changes, as well as requests for additional features supported by this task. A major step will be the establishment of a prototype mechanism for harvesting GitHub contributions on a small subset of selected profiles, e.g., training materials developed using the GitHub template established by the Training Platform. The visualisation of additional statistics for curators both on the APICURON website and via widgets for third-party websites will be supported based on the outputs of WP3.2. In addition, work will be carried out to create appropriate Bioschemas entities for information in APICURON in order to connect to the OpenAIRE knowledge-graph. Activity 2: Engagement and gamification for recognitionThis task focuses on the sociological aspects related to recognition and credit attribution. It will define strategies for implementing gamification effectively, through the evaluation of use cases and establishment of guidelines. The work will span two orthogonal views, from the resources implementing recognition and credit attribution mechanisms (resource view e.g. PomBase) as well as the individual contributors (people view, e.g. curators). The resource view will help define best practices for the granularity of events to be captured in recognition and how to attribute credit for them. The people view will instead focus on how to promote engagement via gamification, i.e. how to build meaningful statistics based on the captured events. Activity 3: Outreach and engagement with other initiativesThis task focuses on promoting alignment with and uptake of the recognition and credit infrastructure by other initiatives, both within and outside ELIXIR (e.g. Bionomia, LifeWatch). It will create opportunities for Community engagement by presenting the recognition work at different ELIXIR meetings (e.g. All Hands Meeting, BioHackathon), and within Platforms e.g. by aligning with related work in the contemporary activities of the Training Platform. It will also provide the necessary coordination with relevant stakeholders for alternative career assessment, including EU projects (such as STEERS, EVERSE and GraspOS) and the EOSC task force on research careers. WP4: Scalable curation support from the long tail of biological dataLead Partners: SIB (Switzerland) The backlog of supplementary data attached to published scientific reports, as well as generalist deposited contents, the so-called long tail of data, is a potential goldmine for research. Unfortunately, these data are buried in the contents of millions of semantically poor files. This long tail of data needs FAIR-ification using automatic methods. Activity 1: Coordination of literature curation challenges and practicesThe primary channel of communication in life science is and remains the literature. However, practices and standards for literature publication are evolving and a growing set of publications contains structured dataset descriptions (e.g., DOME) and links to specialised data repositories or general ones (e.g., Zenodo). Further, and although CDR and Community Databases may exhibit very heterogeneous biological interests, we aim at defining some minimal data typology shared by all data resources: paper- vs. passage-centric curation, continuous vs. session-driven curation efforts, role of supplementary data or generalist repositories in curation guidelines, and named entities as in EuropePMC/SIBiLS annotations. Activity 2: Turning the long tail of literature and supplementary data into FAIR digital objectsThis subtask aims to complement the transformational efforts focusing on the FAIR-ification of literature using semantic web technologies. The idea is to leverage on-going efforts (e.g., PDF2JATS, RO-Crate, DOME, Zenodo) to both improve FAIR archiving standards and to explore how such formats can be discovered through an index or a Knowledge Graph. First, we plan to establish a communication channel with related European initiatives. We will leverage EU research infrastructure projects, such as BiCIKL or FAIRClinical (ELIXIR-LU, CH, FR, UK), to coordinate efforts in and outside ELIXIR with lead stakeholders (e.g., CERN, LifeWatch, GBIF, GBC). Second, the task will explore how these digital objects can be made available for discovery. Activity 3: Accessing traceable author statements from curated databasesELIXIR Core Data Resources and Community Databases tend to cross-reference articles to provide their end-users with access to the source of their knowledge. Unfortunately, the unit of evidence is generally the article, which may mean up to 20-30 pages of PDF. Such granularity is often not sufficient to efficiently access an explicit traceable author statement. However, some databases and communities (e.g. System biology, Rare diseases, Biodiversity) propose to record evidence at a finer granularity. In particular GeneRiFs (Gene Reference Into Functions) and MINT/IntAct can track evidence at the level of a unique sentence. The same applies to biotic interactions. Based on a sample of GBC, CDR and CDB (e.g., DisProt, CelloSaurus, MINT/IntAct, OLIDA), and together with WP3.1, we propose to explore how published evidence could be better captured, cross-referenced and displayed. Such a curation model will leverage methods to uniquely identify both sentences and sections in articles (e.g., Europe PMC SciLite, Biocuration Toolkit); thus evolving article and supplementary data representation standards such as JATS and BioC. WP5: Establishing and shaping the landscape of Core and Community Biological DatabasesLead Partners: Sib (Switzerland), University of Padua (Italy) Activity 1: Leverage the interactions with the Global Biodata Coalition to support the CDR and outreachThe aim of this task is the coordination of the interactions between ELIXIR Data Platform and Global Biodata Coalition. It also includes established processes of assessment for granting CDR/EDD status and Periodic Review of existing resources. Activity 2: Establish guidelines for Community Database identification and monitoringThis task aims to establish a robust and simple procedure for the identification and badging of ELIXIR Community Databases. This entails landscape analysis, covering all ELIXIR Databases, based on Nodes’ service delivery plans (SDPs) to establish simple minimum quality criteria for Community Databases. The identified criteria should be a checklist that does not require additional discussion or complex assessment to be applied. At the end of the process, a first iteration of the ELIXIR Community Database badge should be awarded to all data resources meeting the criteria. Activity 3: Apply and adapt monitoring methodology for indicatorsThe current criteria to define ELIXIR CDR include various bibliometric indicators. Such statistical indicators include the counting of mentions, citations and database accession numbers (e.g., identifiers.org). This acitvity will produce recommendations to establish an improved list of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to support the evaluation of ELIXIR databases. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Beacons
|
Beacons is a technological solution that enables the discovery and sharing of sensitive human data from multiple datasets around the world without compromising privacy. ELIXIR was a major contributor to the development of the Beacon specification, as a product of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health initiative. The technology has now been adopted well beyond Europe, thereby enabling researchers to securely search for and explore the data they need in their work, before undertaking accreditation to have access to them. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Biodiversity Community
|
Biodiversity represents the full spectrum of organisms on Earth, at population, community, and ecosystem levels. The loss and decline of biological diversity are recognised by scientists and the public as a critical challenge for humankind to address. Addressing this global crisis requires knowledge of the diversity of life on Earth, how that diversity functions and interacts, and how it responds to changing environmental pressures. This is why research that transforms our understanding of the variety of life on Earth, at phenotypic or genetic levels, is so important. Current biodiversity data infrastructures and resources are a testament to the long-standing recognition by multiple stakeholders of their importance. However, their heterogeneity poses many challenges. These challenges are both technical, in terms of data analysis and data integration, and at the level of the scientific community, which faces a complex landscape of tools and data that can be difficult to navigate. Building connections across the many infrastructures and services active in biodiversity research is key to overcoming these challenges. These endeavours support the broader ELIXIR framework of striving to bring data science solutions to the priority area of Biodiversity, Food Security, and Pathogens. For more information, have a look at the Biodiversity Focus Group page, as well as the published Biodiversity Community white paper. Goals of the CommunityTo enhance ELIXIR’s network of networks in helping to deliver connected data for biodiversity research
To support the development of standards and promote best practices in biodiversity research
To promote tools and workflows that facilitate reliable and reproducible biodiversity data analyses
To enhance biodiversity database/infrastructure usability and interoperability
To foster knowledge transfer in biodiversity data management and analysis
Leadership
(EMBL-EBI) 
(BSC) 
(SIB) 
(Senior Science Officer, ELIXIR Hub) Find out more |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Call now open: Human Data and Translational Research Linking Data theme
|
The Linking Data theme of the Science tier focus area of the Human Data and Translational Research is now open. Below is all the information you need to apply. Objectives and call requirementsThe Human Data and Translational Research ambition of the ELIXIR 2024–2028 Scientific Programme is to provide the infrastructure to support the discovery, access, sharing and analysis of human genomics data and linked data on a massive scale, building on progress made in this priority area by ELIXIR since 2014. We will achieve our ambition via projects focussed around three themes, which will be implemented as part of the new HDTR project plan. The recently funded projects (from the previous 2024 open call) cover the areas of Data Deposition and Federated Data Analysis. Applicants are now invited to submit their proposals for the Linking Data theme. General information
Linking Data themeData linking is understood to be the technical integration of heterogeneous data sources through identifiers or common attributes, enabling the aggregation, comparison and analysis of data across different domains, formats and structures to enhance data interoperability. Objectives:
Description:The expected outcome is that other data types can be accessed and linked at scale to human genomic data research studies and that relevant data infrastructures and data spaces are interoperable. We encourage proposals that outline specific strategies for linking genomic data with other -omics and heterogeneous data types (for example, imaging), emphasising methods ensuring meta-data alignment. Proposals need to demonstrate achieving interoperability across different ELIXIR Nodes. While it is preferable to use real genomic data, if this is not available then synthetic data will be considered in order to move forward with demonstrating capabilities and solutions. Call requirementsThe ELIXIR Hub will assess proposal eligibility before submitting the proposal for formal review. Applicants will be notified if there are issues with their submission. All steps of assessment, including review panel and evaluation criteria, can be found below. Eligibility:
Proposal details:
Submission process:
Review panel:The Review panel reserves the right to propose small amendments to project budgets or time frames after review, but before issuing funding. This is in order to accommodate the overall restrictions of the call and maximise the number of funded projects. Evaluation criteria:Proposals will be assessed according to the following criteria.
The review process is described in the ELIXIR Guidelines for Commissioned Services, section 3.6 on open calls. In short: reviewers will be allocated to each proposal for assessment and scoring. The scored proposals will be assessed and ranked based on both overall score and alignment with the Science tier ambitions. Find out more
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cancer Data Community
|
Cancer research is highly data intensive, making efficient data management essential to enabling precision medicine for European citizens. The ELIXIR Cancer Data Community was established early in 2024, following the publication of the Community’s white paper. The Community brings together expertise and resources to gather, manage and analyse clinical and biomedical data. By joining forces with other initiatives focused on human data, including several Horizon Europe-funded projects, ELIXIR aims to enhance the data infrastructure, improving the accessibility, quality and interoperability of data, ultimately accelerating discoveries in biomedical research and enabling better decision-making. Effective data management involves the adoption of standardised data formats, robust data privacy and the engagement of healthcare professionals. Broad interoperability of data, metadata, research software and computational infrastructure are all critical for data to make a difference to cancer prevention and treatment. The scope of the Community includes running pilot projects, delivering training and lectures, providing a network of experts to respond to funding opportunities, and influencing the direction of policy development in cancer research. For more information, have a look at the Cancer Data Focus Group page. Community goalsDisseminate existing open solutions
Promote cross-project and cross-initiative collaborations
Design and develop missing community standards
Leadership
(ELIXIR France) 
(ELIXIR Norway) 
(ELIXIR Spain) 
(ELIXIR Hub) Find out more
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Capacity Building and Knowledge Exchange
|
The purpose of the Capacity Building and Knowledge Exchange programme is to strengthen the links between ELIXIR Nodes, facilitate capacity building in ELIXIR Nodes and support the exchange of best practices in bioinformatics service provision. This programme is expected to cover ad-hoc needs, accommodate innovative, emerging ideas, or newly onboarded people requiring capacity building and knowledge exchange outside of the activities already funded through ELIXIR Commissioned Services. The Capacity Building and Knowledge Exchange programme instruments can be applied for with separate forms below. Applications that seek to interact with organisations beyond Europe, in support of implementing ELIXIR’s International Strategy, may also be considered. If interested in submitting such a proposal, in the first instance, the External Relations team at the Hub needs to be contacted. You need to log in to view all the application forms. Travel GrantThe purpose of the ELIXIR Travel Grant Scheme is to support:
Applications must be submitted with at least 30 day’s notice. Due to separate resources already allocated to ELIXIR Nodes, travel to the following meetings are not eligible for Travel Grant:
Travel grants will cover conference registration fees, transportation, accommodation, and subsistence. These will be reimbursed through ELIXIR external expenses. Staff ExchangeThe ELIXIR Staff Exchange allows members of an ELIXIR Node to travel and work in other ELIXIR Nodes, or to attend a specific ELIXIR-related event. The aims of the ELIXIR Staff Exchange programme are to strengthen the links between ELIXIR Nodes, facilitate capacity building in ELIXIR Nodes and support the exchange of best practices in bioinformatics service provision. The Staff Exchange will cover the cost of transportation, accommodation, and subsistence to a maximum budget of €15,000. The applicable rules and regulations of the home institution/Node must be used as a basis for the cost estimation and PM costs of a maximum 1 PM per person. These costs will be reimbursed to the travelling Node through a Proposal of Funding Letter and invoicing after the Staff Exchange has been completed and a report has been submitted to the Hub. Knowledge ExchangeELIXIR supports collaborative partnerships between industry and ELIXIR members to drive innovation in bioinformatics. See the detailed Information of the application process and have a look at previous projects. The Knowledge Exchange will cover the cost of transportation, accommodation, PM costs of a maximum 1 PM per person, and subsistence to a maximum budget of €15,000. These costs will be reimbursed to the travelling Node through a Proposal of Funding Letter and invoicing after the Knowledge Exchange has been completed and a report submitted to the Hub. Please note that ELIXIR cannot fund industry partners in any way. Industry Engagement Days/SME DaysIndustry Engagement Days will give the Nodes a chance to reach out to relevant companies and industry associations, communicate ELIXIR services and forge strong links with the local representatives.
The costs covered for the event will include the venue, catering, and travel expenses to a maximum of €7,000. These costs will be reimbursed to the organising Node through a Proposal of Funding Letter and invoicing after the event, and a report submitted to the Hub.
SME days aim to connect with the international and national industry ecosystem, communicate ELIXIR services and explore opportunities of industry engagement for strategic goals and priorities. You will be eligible if you have previously organised an Innovation and SME Forum. You can apply for the Innovation and SME Forum scheme, maximum budget of €15,000. The costs covered for the event will include the venue, catering, and travel expenses. These costs will be reimbursed to the organising Node/Institute through a Proposal of Funding Letter and invoicing after the event, and a report submitted to and approved by the Hub. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carpentries: about the ELIXIR SWC/DC Pilot project
|
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam, eaque ipsa quae ab illo inventore veritatis et quasi architecto beatae vitae dicta sunt explicabo. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Chose date for TeCG face to face meeting
|
Many ELIXIR kick off meetings are happening in September and October. I agree with many comments in the last monthly meeting and I think we should have our F2F after the kick offs. This would help us to get an update about platforms to better plan our activities. By our F2F we should know if the platforms will have platform coordinators and if so we could invite them to our meeting. I have created a doodle poll with few options to have our F2F meeting. Please vote. I would suggest we have it in Hinxton (UK) on Monday 16-17 Nov collocated with the BioMedBridges Symposium (17-18 Nov) followed by the CORBEL Kick Off (19 Nov). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Collaboration with industry
|
This interactive map provides details of industry engagement by ELIXIR countries. Not shown on the map is EMBL-EBI, the European Node of ELIXIR, which runs a long-standing and successful industry programme. ELIXIR member active in industry; ELIXIR member; Non-ELIXIR member.
ELIXIR Belgium×
ELIXIR Estonia×ELIXIR Finland×
ELIXIR Germany×
ELIXIR Greece×
ELIXIR Italy×
ELIXIR Luxembourg×
ELIXIR Netherlands×
ELIXIR Portugal×
ELIXIR Spain / Spanish National Bioinformatics Institute (INB)×
ELIXIR Sweden×
ELIXIR Switzerland/SIB×
ELIXIR UK×
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commissioned Services
|
Commissioned Services are projects internal to ELIXIR, and funded through ELIXIR's own budget. See the Commissioned Services Guidelines on the intranet. The 2024-2028 Programme will focus on Commissioned Services projects aligning with the programme priorities. See this page for the pre-2024 Commissioned services. Calls now openScience tier
Capacity Building
Pages coming soon:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commissioned Services: Nodes Tier
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commissioned Services: People Tier
|
Developing people and capacity to benefit science and society
PeoplePulseStart date: 1 July 2024 ELIXIR’s continued success requires a dynamic and skilled workforce across all ELIXIR Nodes and roles. This project focuses on these critical aspects of people development:
The PeoplePulse project underscores ELIXIR's commitment to nurturing a skilled, diverse and collaborative community for staff. By addressing key aspects like onboarding, role definition, ELITMa training, equipping ELIXIR Node staff with organisation and management skills and training on impact assessment, ELIXIR aims to strengthen its internal capabilities as well as significantly advance bioinformatics research and innovation. Train the TrainerStart date: 1 July 2024 ELIXIR's goal is to enable and support life science research through the provision of infrastructure, resources, tools, knowledge and skills. Training researchers how to use these resources is essential. The importance of computational biology in life sciences means there’s a myriad of life scientists who could benefit from bioinformatics training. Using a Train-the-trainer approach allows for better scaling of training provision. The project aims to sustain and further develop the community of Train-the-trainer instructors brought together by ELIXIR-GOBLET, develop a mentorship programme and create new training modules that can be delivered by ELIXIR members. ELEAD 2nd Edition: ELIXIR LEadership And Diversity mentoring programmeStart date: 1 January 2025 Building on the success of the ELIXIR Leadership And Diversity Mentoring Programme (ELEAD) Pilot, launched in 2023 to empower women in ELIXIR's middle management with leadership skills, the ELEAD 2nd edition aims to expand this transformative initiative. Running from 2023–2025 as a strategic implementation study, the ELEAD pilot provided a comprehensive training framework, including one-to-one mentoring and peer mentoring professional training on topics such as inclusion, mental health and effective communication. The programme successfully engaged 12 participants from 10 ELIXIR nodes, with senior mentors from within and beyond ELIXIR. Feedback from mentees, mentors, trainers and the broader ELIXIR community gathered at the 2024 All Hands Workshop has shaped the 2nd edition (2025–2027). Key enhancements include:
This enriched ELEAD edition continues to focus on fostering mindful leadership among ELIXIR’s middle management, which remains predominantly occupied by women in roles such as Node Coordinators (NoCs). In contrast, leadership positions like Heads of Nodes (HoNs) and Deputy Heads of Nodes (DHoNs) are still mostly held by men. ELEAD’s goal is to drive progress towards a gender-balanced leadership structure across ELIXIR, promoting a diverse and inclusive environment where all members can thrive. Ambitions:
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commissioned Services: Science
|
The ambitions for the Science tier of the Commissioned Services are:
Biodiversity, food security and pathogensStart date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractIn the priorities of the ELIXIR Scientific Programme 2024-2028, molecular science connecting biodiversity, food security and pathogens has been identified as a societal challenge and scientific opportunity set as a core domain that shapes ELIXIR's activities. The Programme stresses that the application of molecular techniques is critical to understand the diversity and breadth of life on Earth. In other words, the diversity of life, rapidly changing climate, increasing contact between the natural world and humans can influence emerging infectious agents which impact not only humans, but also farmed animals, crops and wildlife. The Commissioned Service contributes to that Priority through the provision of leadership, community engagement, and open project calls:
This effort connects the ELIXIR Communities and Nodes in their response to advances in biodiversity, food security and pathogens and enables these advances to contribute to wider research questions. Cellular and molecular researchStart date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractIn the priorities of the ELIXIR Scientific Programme 2024-2028, leveraging cellular and molecular biology advancements is identified as a core domain that shapes ELIXIR's activities. The Programme stresses bioinformatics and cellular/molecular biology's role in solving global challenges and seeks to build a data-centric infrastructure, requiring strategic planning, partnerships, and funding engagement. The commissioned service contributes to that Priority through the provision of leadership, community engagement, and open project calls:
This effort connects the ELIXIR Communities and Nodes in their response to advances in cellular and molecular research and enables these advances to contribute to wider research questions. Human data and translational researchProposed start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractHuman data and translational research is a high priority for ELIXIR and builds on the progress made in the previous programmes by the Human Data Communities. Within the Science tier of the ELIXIR 2024-2028 Programme, advances will be focussed on enabling researchers (including research clinicians) to use ELIXIR’s infrastructure, for human genomic, phenotypic, imaging and demographic data to support discovery, analysis, innovation and integration of research findings into the clinic and healthcare. More specifically, through our objectives we will ensure:
To further genomics research capabilities, ELIXIR plans to continue to have a lead role in developing data services, management and practices in this area, supported by the ELIXIR platforms, ELIXIR Nodes and externally funded initiatives. By building upon the network of ELIXIR experts we will ensure interoperability across different data spaces and establish a FAIR and federated data ecosystem. Through open calls, community face-to-face meetings, workshops, new community engagements and strategic partnerships we will enable scientists to access, deposit and analyse human genomic data, and to link data on a massive scale to ensure knowledge exchange and interoperability across Europe and beyond. By mapping the needs in the genomic data space in conjunction with scientific groups, Nodes, Communities, and European and International Initiatives, we will join efforts to build a larger infrastructure where data can be securely accessed and used with the aim to improve health and have a positive impact on preventive medicine and healthcare overall. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Commissioned Services: Technology
|
The ambitions of the Technology tier of the ELIXIR Scientific Programme are:
ELIXIR Infrastructure Services (24-TECH-Infraserv)Start date: 1 April 2024 Duration: 33 months AbstractThrough the previous ELIXIR Scientific Programme, a portfolio of key Infrastructure Services has been developed, on which a range of ELIXIR activities depend - the ELIXIR Authentication and Authorisation Infrastructure (AAI), Training e-Support System (TeSS), Beacon Network, and Research Software Ecosystem. This project will provide a new model of core operational, maintenance and governance funding for these services intended to complement feature development funding from other sources. This approach will be combined with active evaluation of the impact and value for money, develop a protocol for managing the portfolio of Infrastructure Services and their selection, and make recommendations for future continuation or modification of the funding model. WP1: To establish a cross-Platform Committee to oversee the portfolio and consider Service development, Governance, Funding, Impact and other aspects.
ELIXIR Compute Platform (2024-TECHNOLOGY-Compute)Start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractThe ELIXIR Compute Platform ensures that European cloud, compute, storage and access services fulfil the requirements and are available for the life-science research community. European regulation on health data processing is evolving, computing capacity in national clouds is increasing and international standards are improving interoperability between the compute environments. Such capabilities are also increasingly important to service the growing volumes of biodiversity, food security and pathogen data which comprise complex data types and must be linked to climate data resources. Also, supercomputer investments - especially EuroHPC - provide completely new kinds of computing capacities for researchers across these domains. All this shapes the landscape of European compute resources. Especially, computing on sensitive data near the data resources is becoming obligatory but the same is true for non-sensitive data e.g. plant phenotyping data and associated imaging data. In 2024-26, the Platform will build technological capability to enable compute in new European-wide federated and multi-cloud settings by building on existing development and utilising previous work, especially Life Science Login. Beyond this, the platform actively seeks sustainable ways to operate the developed services for European researchers. The Platform will deliver the services to support federated data management and analytics in life science through four complementary WPs:
ELIXIR Data Platform (2024-TECHNOLOGY-Data)Start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractThe ELIXIR Data Platform has successfully established a robust community interested in various aspects of life science data, and defined sustainable Core Data Resources (CDRs) of exceptional quality. The Platform is now concentrating on developing and improving methods for brokering data contributions, promoting innovative credit attribution systems, and enhancing and automating data curation practices for FAIRification of existing data. It seeks to expand its work on sustainability to more diverse biological databases and to create a diverse ecosystem of Node Data Resources, fostering collaborations through its extensive ELIXIR member network, while aligning efforts globally and ensuring impactful contributions to European research innovation. ELIXIR Interoperability Platform (2024-TECHNOLOGY-Interoprability)Start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractThe ELIXIR Interoperability Platform's mission has evolved beyond technical and semantic interoperability, responding to changing needs and life sciences standards. It has already created an ecosystem uniting expertise and information. Aligned with ELIXIR's priorities, it introduced peer-reviewed Recommended Interoperability Resources, established the ELIXIR Knowledge Hub, and fostered recognition of Research Data Management (RDM). Now it is transitioning to a sustainable framework for enabling real-world data integration and reuse by promoting and supporting interoperability, data management and FAIR principles. The strategy centres on "The 3 Ps": Products, Processes, and Practices.
These initiatives reinforce the Platform's dedication to interoperability, data stewardship, and efficient resource utilisation. Aligned with Open Science and FAIR principles, they cement the role of ELIXIR in the EOSC ecosystem.
ELIXIR Tools Platform (2024-TECHNOLOGY-Tools)Start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractThe ELIXIR Tools Platform provides services that enable findability, accessibility, interoperability, and reusability of computational tools: including research software, workflows, remote digital services, and trained machine-learning (ML) models. These services aim at being optimised for the needs of molecular life sciences, while at the same time suit a broad range of interdisciplinary applications and scientific communities, including EOSC. The overall goal of the Tools Platform is to sustain the required services and expand them to fulfil the needs of the ELIXIR Programme 2024-2028. The Tools Platform aims to:
The Platform will deliver this work through four Work Packages:
ELIXIR Training Platform (2024-TECHNOLOGY-Training)Start date: 1 January 2024 Duration: 36 months AbstractThe ELIXIR Training Platform (TrP) is building a network of training resources and services, aiming for collaboration, visibility, and standardisation. SPLASH, a digital hub, showcases core services like TeSS, enhancing the training life cycle. Work Packages focus on infrastructure, guidelines, and Train-the-Trainer resources. Collaboration across ELIXIR entities is essential, as are standardised guidelines and a supportive community for knowledge sharing. The project's success will transform training delivery within the community. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
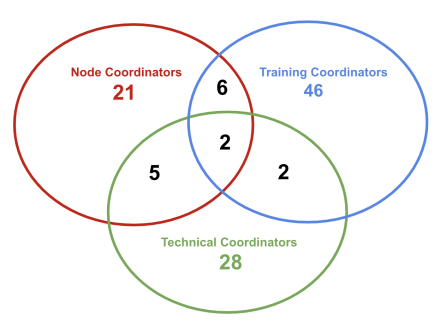
Coordinators triangle
|
Technical Coordinators Group linkThis group promotes connections among Nodes and Platforms, exploring technical opportunities and issues to provide advice and recommendations. Technical Coordinators are often involved in Implementation Studies or Communities. Training Coordinators Group linkConstituting of training representatives of each of theELIXIR Nodes. TrCG meets regularly to share information, expertise and to coordinate and lead the implementation of the ELIXIR training strategy across Europe. Node Coordinators linkThis Group facilitates inter-Node communication on topics relevant to the administrative and operational running of the Nodes. Data Management Coordinators linkEstablished as part of ELIXIR-CONVERGE project (WP1) this group is involved with the development of the Data Management Tooklit (WP3) and in developing best practices to ensure the infrastructure is sustainable in the long term. Activities: The concept of the "Coordinators Triangle" was initially raised at a workshop at the All Hands Meeting in 2021 (document) and picked up at the TeCG (and others) in-person meeting link |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Core Data Resources - Timelines
|
CDR Periodic Review 2024
CDR Annual Indicator Monitoring (AIM) 2024
Support
Information on the Global Biodata Coalition (GBC)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
COVID-19 publications from ELIXIR
|
Publications written by members of ELIXIR Nodes. The papers are ordered by the surname of the first author.
|